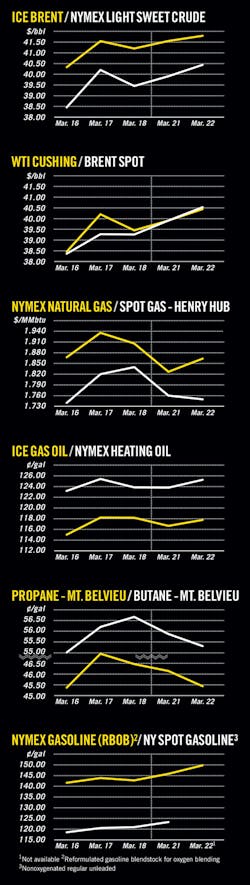
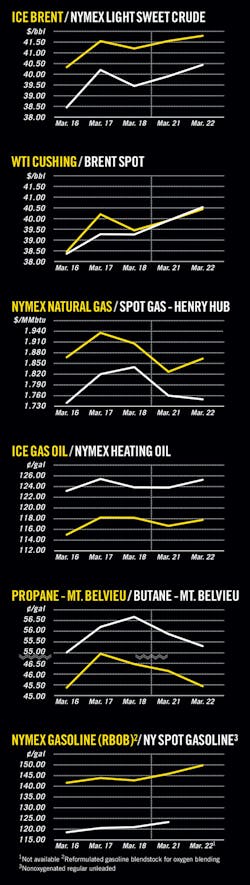
OGJ Newsletter
GENERAL INTEREST — Quick Takes
Barclays: Global E&P spending drop revised down
Barclays has revised down its global exploration and production spending outlook for 2016, now saying such spending could fall 27% this year, down from 15% back in January.
Spending in North America is now trending down 40% vs. 27% in January. International spending is down 21% year-over-year. Since the Barclays Upstream Spending Survey published in January, operators representing 71% of total spending have revised budgets to reflect reduced 2016 spending plans amid a sustained lower oil-price outlook.
"Following a 23% decline in 2015, global spend in 2016 is shaping up to be down a staggering 44% from 2014 levels after the first back-to-back decline since 1986-87. Despite oil prices 48% off the $27/bbl bottom, we believe there is further downside risk to our upstream estimates as Independent E&Ps and [international oil companies] seek to live within cash flow [prior surveyed budgets assumed $50/$45 Brent/WTI] and delay long-term projects," Barclays said.
More than 90% of companies have revised North America E&P spending since January. The expected 40% decline in spending is led by large capitalization E&Ps, down 52%, and small to midsized capitalization E&Ps, down 44%, offset by a more muted 29% decline for US IOCs, which make up 35-40% of the total spending.
Nearly 70% of companies have revised international E&P spending since January and Barclays is now tracking 2016 international upstream spending to decline 21%, driven by IOCs and several national oil companies such as Petroleos Mexicanos (Pemex) -31%, Petroleo Brasileiro SA (Petrobras) -22%, and PetroChina -20%.
Saudi Aramco estimates have also been lowered to -5% from +5% in January.
Eni slashes 4-year capex plan by 21%
Italy's Eni SPA has set group capital expenditures during 2016-19 at $41.78 billion, down 21% from the 2015-18 plan.
The new plan includes a disposal program targeting $7.9 billion of asset sales mainly through the dilution of high working interest stakes in recent material discoveries. In 2015, Eni met 90% of its previous 4-year plan disposal target.
Hydrocarbon production during the 2016-19 period is expected to rise 3%/year, the firm says, explaining the target will be met mainly through the ramp-up and start-up of new projects with a total contribution of 800,000 boe/d in 2019.
Eni expects 1.6 billion boe in oil and gas discoveries during the period while maintaining average exploration spending in line with 2015 levels. Notwithstanding an 18% reduction in overall upstream capex, cumulative production growth of 13% to 2019 is expected.
The firm notes that it has reduced its average breakeven price of new projects to $27/boe from $45/boe, citing portfolio flexibility, ongoing successful exploration strategy, synergies with existing assets, and contract renegotiations.
In its refining segment, Eni plans to address "structural weaknesses" by lowering its breakeven price to about $3/bbl by 2018 while maintaining its current refining capacity, resulting in cumulative cash flow from operations of $3.27 billion over the plan period.
"We are continuing to restructure our mid-downstream businesses successfully," said Claudio Descalzi, Eni chief executive officer. "In refining and marketing, we are focused on lowering our breakeven while enhancing the efficiency of our operations and defending our retail market share."
Petrobras records $9.7-billion loss for 2015
Petrobras reported a 2015 net loss of $9.7 billion, up from a $6-billion loss in 2014.
The final result reflects a record quarterly loss of $10.3 billion during the fourth quarter. During the same period a year earlier, the Brazilian state-owned firm posted a $7.4-billion loss.
Catalysts behind the yearly result were impairments of assets and investments totaling $13.9 billion; exchange losses and interest expenses of $9.2 billion; and an operating loss of $3.5 billion, a decrease of 42% compared with that of 2014.
Petrobras in January slashed planned capital expenditures for 2015-19 by $32 billion from the previously reported amount to $98.4 billion (OGJ Online, Jan. 13, 2016). The new budget assumed an average Brent crude oil price in 2016 of $45/bbl.
A few weeks later, the firm reported that it would shed 14 senior management positions and 30% of 5,300 nonoperational managerial positions as part of the cost-cutting effort (OGJ Online, Feb. 1, 2016).
Exploration & Development — Quick Takes
Study: Liard among world's largest shale resources
The Liard basin in northwest Canada is expected to contain 219 tcf of marketable, unconventional gas, according to a study from five Canadian entities.
The findings were a collaborative effort of Canada's National Energy Board (NEB), the British Columbia Oil & Gas Commission, the Yukon Geological Survey, the Northwest Territories Geological Survey, and the British Columbia Ministry of Natural Gas Development.
The study compares Liard's marketable potential to that of the Montney formation, which has been estimated at 449 tcf; and the Horn River basin, estimated at 78 tcf. Total Canadian gas demand in 2014 was 3.2 tcf, making the Liard basin gas resource equivalent to 68 years of Canada's 2014 consumption.
"However, it is too early to know whether the Liard basin will significantly contribute to Canadian gas production in the near term because gas prices are expected to remain low for the next several years, deterring development," the study notes.
"Although additional in-place gas potential is found in the Horn River shales of the Liard basin, it is uncertain whether any is technically recoverable," it says.
Gas pipelines are present in all three jurisdictions of the basin because of conventional wells that have been producing from Beaver River field in BC since the late 1960s, the Pointed Mountain field and other gas fields in the NWT since the early 1970s, and the Kotaneelee field in Yukon since the late 1970s.
Canada has more than 850 tcf of remaining, marketable gas in areas already served by major pipeline systems. This is the equivalent of 267 years of supply based on Canada's 2014 consumption rate, the study says.
New Zealand offers permits in 2016 tender
New Zealand Petroleum & Minerals (NZPM) has launched its 2016 petroleum block offer, which includes four offshore release areas and one onshore release area collectively covering 525,515 sq km. The areas are:
• The 186,181-sq-km 16NRN-R1 of offshore Northland-Reinga basin.
• The 60,978-sq-km 16TAR-R1 of offshore Taranaki basin.
• The 68,662-sq-km 16PEC-R1 of offshore Pegasus-East Coast basins.
• The 208,632-sq-km 16GSC-R1 of offshore Great South-Canterbury basins.
• The 1,062-sq-km 16TAR-R2 of onshore Taranaki basin.
Bids for Block Offer 2016 must include a work program that demonstrates a technical understanding of the tender area for which a company applies. The invitation for bids for Block Offer 2016 closes Sept. 7. Permits are expected to be granted in December.
New Zealand in December 2015 granted nine petroleum exploration permits covering 429,289 sq km as part of Block Offer 2015.
Most active were OMV AG unit OMV NZ Ltd., which received four offshore permits in the Taranaki basin in partnership with Mitsui E&P Australia Pty Ltd., and Greymouth Petroleum Ltd. unit Petrochem, which took three permits in the onshore Taranaki basin.
New Zealand has run annual block offers since 2012.
NPD sets application deadline for APA 2016
The Norwegian Petroleum Directorate has set a Sept. 6 applications deadline for its 2016 Awards in Predefined Areas (APA) in the North Sea, Norwegian Sea, and Barents Sea. Awards will be announced during first-quarter 2017.
NPD said the program includes 24 blocks in the Norwegian Sea and 32 blocks in the Barents Sea, but did not list a number for the North Sea.
Earlier this year, 56 production licenses were awarded to 36 companies that applied in APA 2015 (OGJ, Jan. 25, 2016, p. 20). A year earlier, 54 licenses were awarded to 43 companies in APA 2014 (OGJ Online, Jan. 20, 2015).
Offshore Abu Dhabi to be evaluated in work program
Austria's OMV AG said it signed a technical evaluation agreement with Abu Dhabi National Oil Co. (ADNOC) and Occidental Petroleum Corp. for several undeveloped oil and gas fields in northwest offshore Abu Dhabi (OGJ Online, Sept. 23, 2015).
The 4-year program involves seismic, drilling, and engineering for exploration, appraisal, and potential field developments, including the Ghasha and Hail areas.
OMV said the agreement intensifies its strategic partnership with ADNOC alongside existing participation in the appraisal of Shuwaihat sour gas field and its east Abu Dhabi exploration activities (OGJ Online, June 24, 2013).
Drilling & Production — Quick Takes
PDO shifting from EOR to lower-cost methods
Petroleum Development Oman (PDO) said enhanced oil recovery (EOR) is expected to account for about 25% of its oil production by 2025, vs. last year's projection of 33% by 2023.
PDO operates several EOR projects, including chemical EOR, miscible gas injection, and thermal applications. But due to lower crude prices and the resource-intensive nature and higher cost of tertiary recovery mechanisms, PDO is placing more emphasis on accelerating conventional oil and gas opportunities instead of short-term expansion of EOR projects.
PDO said 2015 crude oil production of 588,937 b/d was the highest since 2005. Combined production of crude oil, natural gas, and condensate averaged 1.29 million boe/d, which PDO said was a record. Of that total, gas production contributed 83 million cu m/day. PDO accounts for about 70% of Oman's crude oil production and nearly all of its natural gas supply.
In a report on 2015 results, PDO said it made an oil discovery at Sadad North in southern Oman that resulted in 44.5 million bbl of commercial contingent reserves.
A gas discovery at Mabrouk Southwest provided 380 bcf of commercial contingent reserves. It's a satellite to Mabrouk field in the northern part of PDO's Block 6 concession area (OGJ Online, Nov. 19, 2015; Apr. 3, 2013).
A discovery in Tayseer gas field in southern Oman added in-place volumes of 930 bcf of gas and 117 million bbl of condensate, PDO said.
The company also noted that ground-clearing is complete on the 3-sq-km Miraah solar energy project (OGJ Online, July 9, 2015).
Indian firms joining Rosneft for field work
OJSC Rosneft has signed several participation agreements with Indian oil companies expected to boost development of large oil and gas-condensate fields in eastern Siberia.
Through a subsidiary, the Russian company signed a binding agreement under which three state-owned companies, acting jointly as Indian Consortium, will acquire 29.9% participatory share of Rosneft subsidiary Taas-Yuryakh Neftegazodobycha LLC (TYN).
The Indian companies are Indian Oil Corp., Oil India Ltd., and Bharat PetroResources Ltd. BP PLC acquired 20% interest in TYN last November.
TYN operates Srednebotuobinskoye oil and gas-condensate field in the Sakha Republic, Yakutia. The field produces about 20,000 b/d of crude from 50 wells and is connected to the Eastern Siberia-Pacific Ocean (ESPO) oil pipeline with a 169-km spur. It is expected to reach peak production of 100,000 b/d by 2021. The acquisition is expected to close by September.
Indian Consortium also signed a heads of agreement to evaluate the acquisition of a 23.9% interest in Vankorneft, the Rosneft subsidiary that operates Vankor oil and gas-condensate field and the North Vankor license in the Turukhansky district of Krasnoyarsk Territory.
Vankor field produces as much as 440,000 b/d of oil into the 556-km Vankor-Purpe pipeline and is one of the main sources of oil carried by the ESPO line.
The consortium and Rosneft also signed a memorandum of understanding for joint evaluation and possible joint participation in development of Suzunskoye, Tagulskoye, and Lodochnoye oil fields in the Vankor area.
Separately, Rosneft signed a memorandum of understanding with ONGC Videsh Ltd. for an increase in the Indian company's holding in Vankorneft to 26%. ONGC Videsh agreed to acquire a 15% interest in Vankorneft last September in a deal that hasn't yet closed.
The new agreement covers the possible formation of long-term crude-supply deals.
Multistage frac applied at Yuzhno-Priobskoye field
PJSC Gazprom Neft reported performing an 18-stage hydraulic fracturing operation in Russia's Yuzhno-Priobskoye field. Well depth was about 4 km, with the horizontal section extending 920 m. The company said anticipated operational potential is at least 80 tonnes/day of oil, some 15% higher than performance levels following lower-stage fracturing operations.
Gazprom Neft said the key feature was allowing well stimulation to continue throughout its entire operation by using "non-ball-and-socket" well completion and stimulation technology. The company relies on "a special instrument" with a compacted "cushion" that expands and deflates and can be transferred to the next area of the well.
In December, the company reported a 15-stage fracing operation in the same field. Depth of that well was 4.2 km with a horizontal section of 760 m.
Gazprom Neft said the application of multistage fracing also allows a greater proportion of hard-to-recover reserves to be developed by identifying the optimum means of addressing the more marginal areas of a field.
Gazpromneft Khantos, a subsidiary of Gazprom Neft, brought 373 wells into operation in 2015. Some 52 were horizontal wells using multistage fracing (OGJ Online, Feb. 3, 2015).
PROCESSING — Quick Takes
API: US gasoline demand hit new high for February
Total US petroleum deliveries, a measure of consumer demand, gained 2% in February from year-ago levels to average 19.8 million b/d, according to the American Petroleum Institute's monthly statistics. These were the highest February deliveries in 8 years.
"Low gasoline prices continued to drive up demand in February," said Hazem Arafa, API director of statistics. "In fact, gasoline demand rose to a new all-time record for the month as drivers took advantage of the low prices."
Motor gasoline deliveries rose 5.2% from February 2015 to 9.1 million b/d, marking the highest deliveries for the month on record. February distillate deliveries were down from the prior year by 17% to average nearly 3.8 million b/d.
Crude oil production fell 3.6% from February 2015 to average 9.1 million b/d last month.
US total petroleum imports for the month averaged nearly 9.9 million b/d, up 6.7% from year-ago levels. Refined product imports in February increased 6.1% to 2.3 million b/d.
In February, gasoline production averaged 9.9 million b/d, up 3.2% from year-ago levels, while distillate fuel production declined 3.3%. API's latest refinery operable capacity was 18.174 million b/d. Refinery gross inputs increased 1.7% from February 2015 to reach a new high for the month, averaging 15.9 million b/d.
Exports of crude oil and refined products increased 6% to average just below 5 million b/d-the highest February export level ever.
Crude oil stocks ended February at 519.6 million bbl, up 16% from a year ago to the highest February inventory level since 1930. Stocks of motor gasoline ended the month at 252.4 million bbl, up 4.9% from the prior year. Distillate fuel oil stocks rose 32.2% from the same period last year to end at 162.8 million bbl-the highest February inventory level in 35 years. Jet fuel stocks rose 10.2% to end at 42.5 million bbl. Stocks of "other oils" were down from year-ago levels.
CNOOC-Shell JV take FID on ethylene expansion
Shell Nanhai BV and China National Offshore Oil Corp. have taken final investment decision on the companies' previously announced plan to expand capacity at their 50-50 joint venture CNOOC & Shell Petrochemicals Co. Ltd.'s (CSPC) petrochemical complex in the Daya Bay Economic and Technological Development Zone, Huizhou, Guangdong Province, China.
As part of the Mar. 21 FID, which follows a heads of agreement signed by the partners in late 2015, CSPC will take over CNOOC's current project to build additional chemical production installations adjacent to the CSPC's existing Nanhai petrochemical complex, the companies said.
Alongside ongoing construction of an ethylene cracker and ethylene derivatives units that will increase ethylene capacity by more than 1 million tonnes/year, or about double the complex's current capacity (OGJ Online, Dec. 20, 2013), the expansion also includes construction of what will be China's largest styrene monomer and propylene oxide (SMPO) plant.
The expanded complex, once completed, will use Shell's proprietary OMEGA, SMPO, and Polyols technologies for the first time in China to produce the following: ethylene oxide, 150,000 tpy; ethylene glycol, 480,000 tpy; and high-quality polyols, 600,000 tpy.
In addition to improving the complex's overall energy efficiency and quality of production, the expansion complements CSPC's aim of meeting China's growing domestic demand for petrochemical products, CNOOC and Shell said.
Current production capacities at the Nanhai complex include: ethylene, 950,000 tpy; propylene, 500,000 tpy; butadiene, 165,000 tpy; low-density polyethylene, 250,000 tpy; high-density polyethylene, 260,000 tpy; polypropylene, 260,000 tpy; monoethylene glycol, 350,000 tpy; styrene monomer, 640,000 tpy; propylene oxide, 290,000 tpy; polyols, 170,000 tpy; and propylene glycol, 60,000 tpy.
Croatian refinery due energy efficiency study
Croatia's INA Industrija Nafte DD, Zagreb, has let a contract to Neste Jacobs Oy to perform a comprehensive energy efficiency study of its 4.5 million-tonne/year Rijeka refinery along the northern part of the Adriatic Sea at Urinj, Croatia.
The goal of the study is to deliver a review of existing energy consumption, energy sources, and energy producing and consuming assets within the refinery and associated logistics terminal area in order to identify possible improvements compatible with INA's ISO 50001:2011 certified energy management system, Neste Jacobs said on Mar. 22.
The energy efficiency study follows INA's 2015 announcement that it would carry out a more than $400-million residue upgrade program at Rijeka to improve the refinery's market competitiveness by increasing conversion of the site's existing production to lighter, more valuable products such as LPG, gasoline, and diesel (OGJ Online, July 7, 2015).
The residue upgrade project at Rijeka comes in the wake of a series of modernization efforts INA has undertaken at its two Croatian refineries over the last few years.
Most recently, INA let a contract to Duro Dakovic Industrijska Rjesenja DD, a subsidiary of Djuro Djakovic Holding DD, to build and deliver two columns for an LPG amine treatment unit to be built at the Rijeka refinery (OGJ Online, Feb. 16, 2016).
TRANSPORTATION — Quick Takes
Gorgon off Western Australia ships first LNG cargo
The Chevron Australia Pty Ltd.-led joint venture at the Gorgon and Jansz-Io field project on Barrow Island offshore Western Australia has shipped its first cargo of LNG.
The shipment is bound for Chubu Electric Power Co. Inc. in Japan, one of Chevron's foundation customers.
The vessel concerned is the Asia Excellence, one of Chevron's new state-of-the-art carriers.
The $54-billion Gorgon project is being supplied with gas from Gorgon and Jansz-Io fields in the Greater Gorgon region between 130-220 km off northwestern Western Australia.
The facilities on Barrow Island are capable of producing 15.6 million tonnes/year of LNG. They also include a carbon dioxide injection project and a domestic gas plant-the latter with capacity to supply 300 terajoules/day of gas to market.
More than 80% of Chevron's share of the gas from Gorgon and neighbouring Wheatstone projects-which is due to come on stream in mid-2017-is covered by long-term sales contracts with customers in the Asia-Pacific region.
Pembina Pipeline to buy Kakwa gas complex
Pembina Pipeline Corp. has agreed to acquire sour gas processing properties in the Musreau area of Alberta from Paramount Resources Ltd. for $556 million (Can.) cash and other consideration pushing the transaction value to more than $600 million (Can.). Both companies are based in Calgary.
Pembina will acquire Paramount's new Kakwa gas processing complex and associated facilities including gas-gathering pipelines, a sales-gas pipeline, and future disposal wells as well as information and rights for a possible gas processing plant designated 6-18.
The Kakwa complex has raw-gas processing capacity of 250 MMcfd, including a 200-MMcfd deep-cut train, a 50-MMcfd shallow-cut train, and 22,500 b/d of condensate stabilization.
It's connected by pipeline to Pembina's Cutbank Complex about 15 km away. Combined, the facilities will have more than 1 bcfd of processing capacity.
The 6-18 facility, for which Paramount has secured site licenses and performed preliminary engineering, would be a shallow-cut plant about 7 km from the Cutbank Complex