WoodMac: Global upstream challenges to compound in 2023
Upstream oil and gas companies made progress restoring confidence and repairing balance sheets in 2022, but challenges the industry faces will compound in 2023, according to a recent Wood Mackenzie report.
Themes to watch include windfall taxes, restrained investment growth, cost inflation, and business model changes.
Windfalls, incentives
Country risk has risen as an investor consideration. If prices move higher, more countries will act on price caps or windfall taxes. Operators will have to reassess current and new opportunities, even in countries previously thought to be low risk.
“We will see many different approaches, from windfall taxes to relieve pressure on public finances, to incentives which accelerate oil and gas potential” said Fraser McKay, head of upstream analysis at Wood Mackenzie. “Many of these actions will begin to reflect the energy transition aspirations of host governments. We advocate smart policies which provide both fairness and predictability, regardless of the prevailing price.”
Restrained investment growth
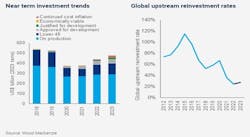
The report forecasts global upstream cash flow will fall 9% to $1.3 trillion in 2023, while reinvestment rates (investment divided by operating cash flow) will rebound to 28%, up from an all-time low of 24% in 2022. Development spending will increase as well, up at least 10% to $460-480 billion.
Said McKay, “Investment needs to rise further in 2023 and subsequent years if supply shortages are to be avoided. But not by as much or for as long as many market observers think. And with corporate deleveraging largely complete, there is room for both incremental reinvestment and continued shareholder distributions. Who increases spend, where and by how much will be a much-debated topic in 2023.”
Cost inflation will constrain the impact of spend increases, and supply chain bottlenecks and inefficiencies will threaten the gains made through previous downturns, the report said. About half of the global increase in spend will be consumed by widening supply chain margins.
Decarbonization
According to the report, governments and national oil companies (NOCs) in the main producing countries will try to marry low-carbon credentials with increasing upstream investment in 2023. International oil companies (IOCs) will also need to demonstrate and disclose further emissions reductions.
McKay stated: “Regulations will compel companies to invest in measurement, monitoring and mitigation. Those that have already tackled the low hanging fruit will need to dig deeper – electrification and grid connection where it’s possible, dedicated renewables where it’s not. By the end of 2023 it will be extremely hard for mainstream operators to sanction projects without emissions mitigation plans.”
Gas business models
The European gas crisis triggered price spreads that will push upstream operators to reassess gas business models. Near-term investment will focus on raising domestic European production and new development concepts to unlock stranded gas.
“We won’t see the industry spending more on gas than oil this year, but it’s clear that gas remains investible and will play an important role for upstream companies moving forward,” said McKay. “This year, operators will focus on making gas project returns more competitive with oil, while evaluating carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS) for high CO2 content fields and even blue hydrogen concepts.”