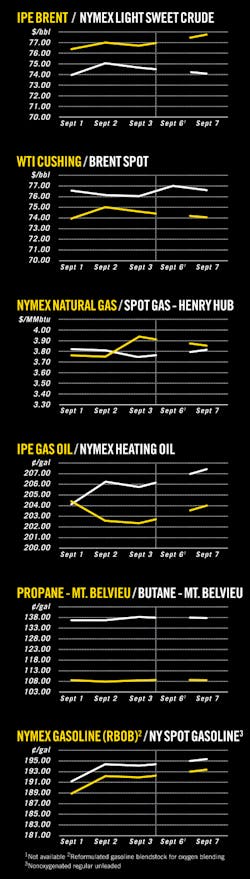
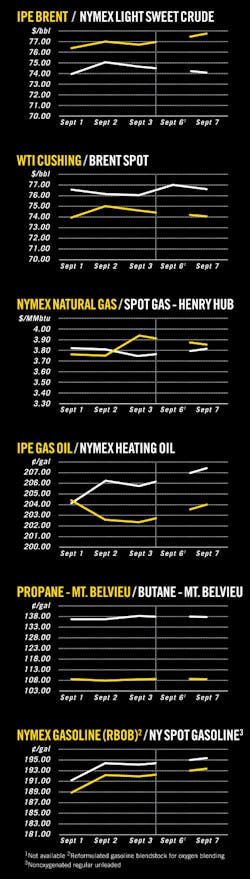
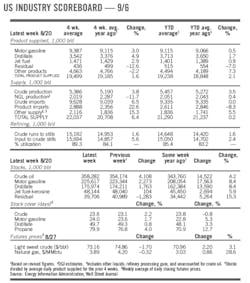
OGJ Newsletter
OTC: Panel provides views on oil spill prevention
Restoring public trust and setting new standards are vital to moving forward in the oil and gas industry, according to David Payne, Chevron Corp.'s vice-president, drilling and completions.
Speaking at a panel discussion May 3 at the Offshore Technology Conference in Houston, Payne noted, "The industry today is much safer than it was Apr. 20," referring to the date last year when BP PLC's deepwater Macondo well blew out, setting fire to and sinking the Deepwater Horizon semi, and spilling millions of barrels of oil into the Gulf of Mexico.
Payne discussed three elements that are important in prevention: human interface data, training, and procedures. He stressed that having a checklist is important to improve decision-making processes in an emergency.
The panel provided different perspectives on prevention and effects of the spill. Hanadi Rifai, director of environmental engineering, University of Houston, provided an academic perspective by discussing the effects on natural resources. Rifai stressed that prevention was key and attenuation and recovery are not guaranteed.
Martin Massey, chief executive officer, Marine Well Containment Co., focused his comments around preparation. "We need to continuously be ready to respond to a well control incident in the deepwater Gulf of Mexico."
Christopher Smith, deputy assistant secretary for oil and natural gas with the US Department of Energy, remembered the 11 lives lost by taking a moment to display their names.
OTC: Nova Scotia maps play fairway to attract explorers
Nova Scotia is preparing to make public the results of 2 years of research into the complex geology of the province's Atlantic shelf and slope in a move to attract explorers to an offshore bid round to be held as early as late 2011.
The soon-to-be-released play fairway analysis is the product of $15 million in extensive geoscience research and may be the first time an effort of such scope has been applied outside an exploration company. The results are to be made available electronically without charge to oil and gas exploration companies, said R.A. MacMullin, director, Nova Scotia Department of Energy.
Beicip-Franlab, Paris, has integrated the inputs of research into plate tectonics, biostratigraphy, geochemistry, seismic reprocessing, salt structural interpretation, and reservoir quality into the finished analysis.
The group is about to publish a digital atlas of montages of maps derived from the various scientific analyses, MacMullin said May 4 at the Offshore Technology Conference in Houston.
Among other things, the research turned up solid evidence of two Jurassic source rocks, he said. The northeastern part of the 500-mile-long study area appears more gas-prone, while the southwestern part seems more oil-prone, he added.
A biostratigraphic project that is one of the 10 special projects in the play fairway analysis was undertaken by the Offshore Energy Technical Research Association, Halifax, said Jennifer Matthews, research manager.
Funds for the analysis came from the Department of Energy and originated as forfeiture payments made a decade ago by companies which, having drilled dry holes, relinquished exploration licenses before they expired. The department launched the play fairway analysis as it sought to explain the early departures and determine what might rekindle interest.
Japan eyes changes in energy policy
As part of a review of the nation's growth strategy, Japan is considering a drastic shift in its energy policy to better deal with the consequences of the Mar. 11 earthquake, tsunami, and nuclear crisis.
"The growth strategy, mainly its energy environment policy, must be transformed in quality," said Koichiro Gemba, Japan's national policy minister, referring to policies developed in June 2010.
Under that growth strategy, Tokyo aimed to have the nation's economy expand a real 2% or more on average by fiscal 2020, by focusing budgetary allocations and accelerating deregulation on seven designated areas such as energy and the environment.
Under the revised growth strategy, however, Japan reportedly will put more emphasis on the development of renewable energy such as power generated by solar, wind, and geothermal heat, as well as the enhancement of electric accumulators.
More to the point, Japan will seek to secure electricity without depending on nuclear power too much.
Government sources said projects for exporting nuclear power plant technologies will "inevitably" be revised as a perception is prevailing among government officials that it would be difficult for a country which let a nuclear crisis happen to sell such plants overseas.
Last October, Japan agreed with Vietnam to construct two nuclear power plants, and it has been in negotiations with Turkey for similar exports. But Tokyo may halt such projects at least until Japan completes its investigation of the radiation leakage at nuclear facilities damaged after the earthquake and tsunami.
Chevron to buy Marcellus acreage from Chief
Chevron Corp. will expand its acreage holding in the Marcellus shale gas play of the eastern US with the purchase of gas properties from Chief Oil & Gas LLC, Dallas, and Tug Hill Inc., a private investment firm in Fort Worth.
The primary asset covered by the purchase agreement is a lease position of 228,000 net acres, mainly in the southwestern part of the play in southern Pennsylvania.
Chief and Tug Hill will retain 125,000 acres of Marcellus shale leasehold in Bradford, Susquehanna, Tioga, Sullivan, and Wyoming counties of northeastern Pennsylvania. Chief said it plans to remain active in the play.
Chevron entered Marcellus shale development with the acquisition, closed in February, of Atlas Energy, Pittsburgh, for $3.2 billion plus assumption of $1.1 billion debt (OGJ, Nov. 15, 2010, Newsletter).
That acquisition included 486,000 net Marcellus acres and a 49% interest in Laurel Mountain Midstream LLC, which owns more than 1,000 miles of gas pipelines and gathering lines in the region.
Chevron became operator of a Marcellus joint venture Atlas formed earlier last year with an affiliate of Reliance Industries Ltd., Mumbai, assuming the acquired company's 60% interest.
The Chief-Tug Hill purchase aligns with Chevron's plans "to acquire early-in-life assets with long-term organic growth potential," said George Kirkland, vice-chairman. Over the last year, the company has acquired nearly 5 million net acres of shale-gas assets in the US, Canada, Poland, and Romania.
Eni, Sonatrach target Algerian shale gas
Eni SPA and Algeria's state-owned Sonatrach have signed a cooperation agreement for development of unconventional hydrocarbon resources, "with particular focus on shale gas," according to an Eni press statement.
The companies provided no specifics, saying they will "jointly implement activities to assess the technical and commercial feasibility of exploration and operational initiatives in shale gas."
A recent assessment by the US Energy Information Administration listed Algeria among countries in which shale-gas development is likely to emerge because of resource assessments exceeding 200 tcf (OGJ, Apr. 4, 2011, p. 22).
Eni, already active in Algeria, said it "confirms the significant shale gas reserves in Algeria which Eni and Sonatrach wish to explore and develop."
Drilling & Production — Quick TakesExxonMobil to develop Hebron oil field off Canada
ExxonMobil Canada Properties filed a development plan with Newfoundland and Labrador authorities in mid-April to develop Hebron oil field in the Atlantic off eastern Canada.
Forecasted cumulative recovery over 30 years is estimated at 660-1,055 million bbl of oil. Development would be via a gravity base structure with 52 well slots and the capacity to store 1.2 million bbl of oil in multiple compartments.
Topsides will be designed for oil production of 150,000-180,000 b/d of oil and 200,000-350,000 b/d of water. Oil production could begin in mid-2017 if the project were sanctioned in mid-2012.
The plan filed with the Canada-Newfoundland and Labrador Offshore Petroleum Board said Hebron will be the fourth stand-alone development on the Grand Banks and, considering the Hibernia and White Rose tieback project, the sixth offshore oil project.
Hebron is in 88-102 m of water 9 km north of Terra Nova field, 32 km southeast of Hibernia field, and 340 km off St. John's. It consists of Hebron, West Ben Nevis, and Ben Nevis fields on four significant discovery licenses: SDL 1006, 1007, 1009, and 1010.
Hebron was discovered in 1980, but the field area wasn't proved commercial until the mid-1990s, ExxonMobil said.
The asset is composed of four reservoir intervals in several normal fault-bounded fault blocks. The four stratigraphic units are the Late Jurassic Jeanne d'Arc formation and the Early Cretaceous Hibernia, Avalon, and Ben Nevis formations. The asset has five major pools although other hydrocarbon-bearing pools beyond these exist.
The Ben Nevis reservoir in Hebron field is expected to produce 80% of the project's crude oil, but the 20° gravity oil presents production challenges with viscosity 10-20 times that of water.
The Jeanne d'Arc and Hibernia reservoirs at Hebron and the Ben Nevis reservoir at West Ben Nevis and Ben Nevis fields are also significant resources.
Relative to the Hebron Ben Nevis reservoir, the Jeanne d'Arc and Hibernia reservoirs have higher oil quality but decreased reservoir quality consistent with deeper burial and cementation. The Jeanne d'Arc formation has lower reservoir quality than the Jeanne d'Arc formation at Terra Nova field, just as the Hibernia formation at Hebron has lower reservoir quality than the Hibernia formation at Hibernia field.
Associated gas will be used to fuel production and drilling facilities. When gas volumes exceed those needs, surplus gas will be injected into one of the reservoirs for storage and pressure maintenance. Stored gas may be withdrawn if the produced gas rate falls below volumes needed for platform operations. Gas handling facilities will be designed for 215-300 MMscfd of associated gas and gas-lift gas.
Hebron interest owners are ExxonMobil Canada operator with 36.0429%, Chevron Canada Ltd. 26.628%, Petro-Canada Hebron Partnership 22.7289%, Statoil Canada Ltd. 9.7002%, and Nalcor Energy—Oil & Gas Inc. 4.9%.
Shell starts production from Scotford upgrader
Shell Canada Energy has started production from the Scotford upgrader expansion project near Edmonton. The 100,000 b/d expansion increases Scotford's bitumen upgrading capacity to 255,000 b/d.
Shell produces the bitumen at its Muskeg River and Jackpine mines in the Athabasca area of northeast Alberta.
The company notes that its engineers will now focus on improving operating efficiencies and adding capacity through debottlenecking.
Shell also continues design and engineering work on the proposed Quest carbon capture and storage project at the Scotford upgrader for potentially capturing and storing underground about 1 million tonnes/year of carbon dioxide. It expects to make a final decision on starting construction on the project in 2012, after obtaining all regulatory approvals.
Operator Shell Canada Energy holds a 60% interest in the Athabasca Oil Sands Project (AOSP). Its partners are Chevron Canada Ltd. 20% and Marathon Oil Corp. 20%.
AOSP includes the Muskeg River mine, Jackpine mine, and Scotford upgrader.
Eurasia Drilling, Schlumberger swap assets
Eurasia Drilling Co. Ltd. (EDC) and Schlumberger have completed an exchange of drilling and servicing assets in Russia and formed an alliance to cooperate on services to EDC.
EDC bought from Schlumberger 19 drilling rigs with 17 crews, 34 workover rigs with 25 crews, and 23 sidetracking rigs with 20 crews, most operating in West Siberia for Russian oil companies Rosneft, TNK-BP, GazpromNeft, and Lukoil.
Schlumberger bought from EDC drilling services assets including directional drilling, cementing, and drilling fluids engineering and materials supply. The purchase includes 24 cementing crews, 57 directional drilling and telemetry crews, and 50 crews for drilling fluids.
Under the strategic alliance, the firms will cooperate on supply of oil and gas services to EDC for 5 years.
Total value of the deal is $260 million, including a cash consideration of $173 million from EDC to Schlumberger.
PROCESSING — Quick TakesBP, Davy move FT process toward market
BP PLC and Davy Process Technology, London, have taken a step toward moving their technology for converting synthesis gas into a range of liquid products to the commercial market.
The companies have signed agreements to work individually with three engineering firms to promote commercialization of the BP/Davy Fischer-Tropsch (FT) process.
The agreements are with CB&I Lummus UK Ltd., Jacobs Engineering Group Inc., and Shaw Group.
BP and Davy have demonstrated their fixed-bed technology at a 300-b/d plant at Nikiski, Alas., which went on stream in 2002, and have made the process available for license.
Collaboration with the engineering firms, said Mark Howard, BP vice-president for conversion technology, "will help with the early identification and evaluation of opportunities and ensure the availability of first-class engineering resources familiar with our process to support potential licensees."
The BP/Davy process uses FT conversion of syngas, a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide, to produce diesel, jet fuel, and naphtha. Syngas can be produced from natural gas, biomass, or coal.
Technip to expand CNRL's Horizon upgrader
Canadian Natural Resources Ltd. has let an engineering, procurement, and construction support services contract to Technip for expansion of the delayed coking unit at its Horizon bitumen upgrader in Fort McMurray, Alta.
Technip said value of the contract is about €100 million. Work is to be complete in 2013.
CNRL is expanding the Horizon oil sands mining and bitumen extraction project, now with capacity to produce 110 million b/d of 34° gravity synthetic crude oil (SCO), in phases to 232,000-250,000 million b/d.
In work it describes as reliability projects, it is adding 5,000 b/d of SCO capacity through 2014, this year completing a third ore preparation plant, hydro transport, and tank expansion.
The coker expansion, coupled with debottlenecking, will add 10,000 b/d of SCO capacity by 2014.
Future work will include a fourth ore preparation plant, vacuum distillation, and gas-oil hydrotreatment, combining for 45,000 b/d of incremental SCO capacity, followed by a fifth ore preparation plant, a third and fourth extraction unit, a combined hydrotreater, and sulfur recovery, adding 80,000 b/d of SCO capacity.
CNRL estimates proved and probable reserves at the Horizon project at 2.9 billion bbl of SCO and bitumen initially in place at 14.3 billion bbl.
Nippon Oil resumes shipments at Sendai refinery
JX Nippon Oil & Energy Corp. May 3 resumed shipments of products from its Sendai refinery for the first time since the facility was damaged during the Mar. 11 earthquake that hit Japan.
The refinery's daily shipment capacity of gasoline, kerosine, and other products stands at 2,500 kl, about 50% of its output before the quake. Refining operations remain offline at Sendai facility, however, and the products being shipped are from existing inventory.
The JX Holdings Inc. unit installed equipment to load nine tanker trucks at the same time, and it plans to begin accepting ships by May 8 to strengthen its supply capabilities within Miyagi Prefecture and other areas.
A refinery official said the facility is to increase its shipping capacity to a minimum 5,000 kl/day before winter to satisfy peak demand for heating oil and other products.
The company's refining facilities in Sendai, which were badly damaged during the earthquake, are not expected to resume operations until mid-2012.
ExxonMobil Corp.'s Shiogama Terminal in Sendai reopened Mar. 20 and received its first tanker shipment of fuel, including 2 million l. of gasoline, light oil, and kerosine.
"The terminal is a key distribution point for the impacted area and is also being used by other companies to bring in needed supplies," an ExxonMobil spokesman told OGJ (OGJ Online, Mar. 22, 2011).
TRANSPORTATION — Quick TakesOneok to build NGL pipeline, fractionator
Oneok Partners LP, Tulsa, will invest between $910 million and $1.2 billion to build out its NGL infrastructure along the Texas Gulf Coast.
Between now and late 2013, the company will:
• Build a 570-mile, 16-in. OD NGL pipeline—the Sterling III Pipeline—to move unfractionated NGLs or NGL purity products from the US Midcontinent to the Gulf Coast.
• Reconfigure its existing Sterling I and II NGL distribution pipelines.
• Build a 75,000 b/d NGL fractionator, calling it MB-2, at Mont Belvieu, Tex.
Oneok Partners Chief Executive Officer Terry K. Spencer said the projects are to accommodate growing NGL production in the Midcontinent and elsewhere and help "alleviate the infrastructure constraints" between Midcontinent and Gulf Coast markets.
The Sterling III pipeline will cost $610-810 million and have an initial capacity of 193,000 b/d from the partnership's NGL infrastructure at Medford, Okla., to storage and fractionation at Mont Belvieu. Once completed, it will double the partnership's current pipeline capacity between Medford and Mont Belvieu, said the company announcement.
The investment also includes reconfiguring the existing Sterling I and II pipelines, which currently carry NGL purity products between the Midcontinent and Gulf Coast, to transport unfractionated NGLs or NGL purity products.
Construction will begin in early 2013, following receipt of necessary permits and the acquisition of right of way. The partnership anticipates using a portion of the existing ROW on the Sterling I and II pipelines. Completion is slated for late 2013.
With additional pump stations, Sterling III Pipeline's capacity can be expanded to 250,000 b/d, said the company. It will cross the Woodford shale as well as provide transportation capacity for NGL production from the growing Cana-Woodford shale and Granite Wash, where it can gather unfractionated NGLs from new natural gas processing plants that are being built in response to increased drilling in these areas.
The new MB-2 fractionator will cost $300-390 million to build and will supplement the partnership's 80%-owned, 160,000-b/d MB-1 fractionator in Mont Belvieu. Its initial 75,000-b/d capacity can be expanded to 125,000 b/d to accommodate additional NGLs as they are added to the currently expanding Arbuckle Pipeline and the new Sterling III Pipeline and the Sterling I and II reconfiguration.
Gorgon applies for fourth Barrow Island LNG train
Chevron Australia has applied for environmental approval for a fourth LNG train on Barrow Island. The company says it has found sufficient gas to support such a move and that it plans to begin front-end engineering and design work on the extended Gorgon project in 2012. This could lead to a final investment decision on the fourth train towards the end of 2013 and the start of construction in 2014.
Under the environmental approval application, Chevron is seeking approvals for Train 4, a gas pipeline system, and a horizontal directionally drilled shore crossing. It is also seeking approvals for offshore subsea production infrastructure that could include 38-63 producing wells.
Chevron says the fields most likely to be considered for the Barrow Island plant extension include Yellowglen, Chandon, Satyr, Achilles, Maenad, Orthus, Geryon, Dionysus, Dionysus North, Chrysaor, and West Tryal Rocks.
A number of these are relatively recent discoveries while others have been waiting commercial development since the 1990s and earlier.
The proposed feed gas pipeline system from these fields will cross both federal and state waters to reach Barrow, but the route won't be finalized until the completion of technical, environmental, safety, and economic performance evaluations.
The onshore component of the pipeline system will lie within the foundation three-train Gorgon project easement to connect to the gas treatment plant being built on the east coast of the island.
Chevron says the 50 ha of ground required for a fourth train and its associated facilities has already been cleared for the initial Gorgon work, although it may require an additional 10 ha for the pipeline shore crossing and other onshore components of the pipeline.
Nevertheless this area is included within the 300 ha made available under the Barrow Island Act.
Construction and operations workforce will be accommodated in the village already assessed and approved for the foundation project.
More Oil & Gas Journal Current Issue Articles
More Oil & Gas Journal Archives Issue Articles
View Oil and Gas Articles on PennEnergy.com