OGJ Newsletter
Marcellus coming of age, says Range Resources
The initial rate averaged 7.3 MMcfd of gas equivalent for 10 horizontal Devonian Marcellus shale wells brought online since October 2008 into a new gas processing plant in western Pennsylvania, said Range Resources Corp., Fort Worth.
The Marcellus, a hindrance to overall capital efficiency in the past few years, will be “highly accretive to our capital efficiency in 2009,” the company said.
Seven of the 10 wells had initial rates of 3.5 MMcfd of gas equivalent or more, and three flowed 9 MMcfd of gas equivalent or more. The best well made 24.5 MMcfd of gas equivalent.
The company is producing 35 MMcfd of gas equivalent from the Marcellus and is constrained by processing capacity. Eight of the wells have been on line for more than 30 days, and their 30-day average rate is 4.3 MMcfd of gas equivalent. The highest volume well averaged 9.6 MMcfd of gas equivalent.
Processing capacity is expected to expand to 60 MMcfd in late March or early April and to 180 MMcfd by late 2009-early 2010. Target 2009 exit rate is 80-100 MMcfd net to Range.
A built-for-purpose rig is to arrive later in January, the first of six that will replace existing rigs, and Range plans to exit 2009 with six rigs running in the play.
Range, which has cut more than 20 days and $800,000 from its drilling costs in recent wells, believes horizontal well costs will average $3-4 million in 2009.
Taking advantage of a streamlined permitting process, the company has a majority of its 2009 drilling permits in hand and has secured water withdrawal and disposal capacity for several years.
Baker Hughes reported 23 rigs active in Pennsylvania in the week ended Jan. 16, compared with averages of 16 in 2007 and 23 in 2008, when the state’s count peaked at 30 in the week ended Nov. 7.
Future demand buoys Canadian shale, LNG projects
The US Energy Information Administration sees Canadian gas shale formations as an increasingly important part of US natural gas imports in 2009. In its “US Natural Gas Imports and Exports: 2007” special report published this month, EIA cited renewed interest and optimism regarding unconventional gas recovery in Canada following the successes seen in the northeast Texas Barnett shale and other formations in the Lower 48 states.
EIA estimated 2007 production in the Upper Montney region of British Columbia at 80 MMcfd of gas and expects this to rise rapidly in 2009. The report listed Encana Corp., Apache Corp., and EOG Resources Inc. as having listed reserves in the area. Wood Mackenzie Ltd., however, forecast recently that the market could be adequately supplied without developing “expensive or challenging” shales such the neighboring Horn River (OGJ, Dec. 8, 2008, p. 32).
EIA also cited other Canadian efforts toward meeting future increases in North American demand, including Irving Oil Ltd. and Repsol-YPF SA’s Canaport LNG terminal in New Brunswick. The terminal is Canada’s first and will be used to meet demand in the US northeast and eastern Canada starting early 2009. Construction of three 2.5 bcf storage tanks is complete. Total sendout capacity is 1.2 bcfd, with the first phase of operations using existing and expanded capacity on the Maritimes & Northeast Pipeline to move gas into the US.
DOE makes first direct oil buys for SPR since ‘94
The US Department of Energy awarded contracts on Jan. 16 to purchase nearly 10.7 million bbl of oil for the Strategic Petroleum Reserve. The awards were the first direct purchases of crude for the reserve since 1994, it said.
DOE said it awarded the contracts to Shell Trading Co. and to Vitol Inc. to deliver oil to the SPR from February to April. It said that it used revenues from the emergency sale of crude from the reserve following Hurricane Katrina in 2005 to pay for the purchase.
DOE also announced contracts using the royalty-in-kind transfer program with the US Department of the Interior to Shell Trading and Glencore Ltd. for 26,000 b/d of oil.
These awards will result in the addition of nearly 6.16 million bbl of oil to the SPR’s inventory from May 2009 through January 2010, DOE said.
It said both sets of awards resulted from separate contract solicitations on Jan. 2. DOE said it decided to solicit the oil following sharp price declines during second-half 2008, which made the purchases more economically favorable.
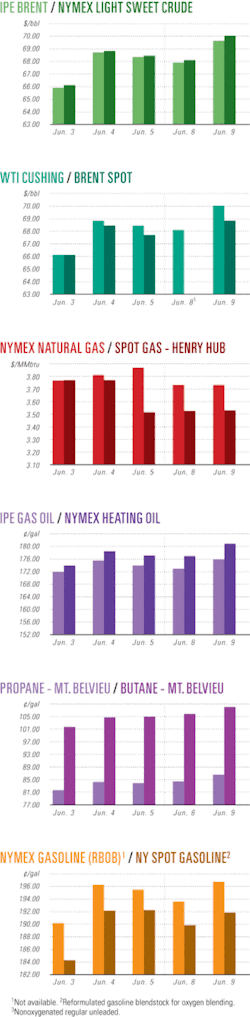
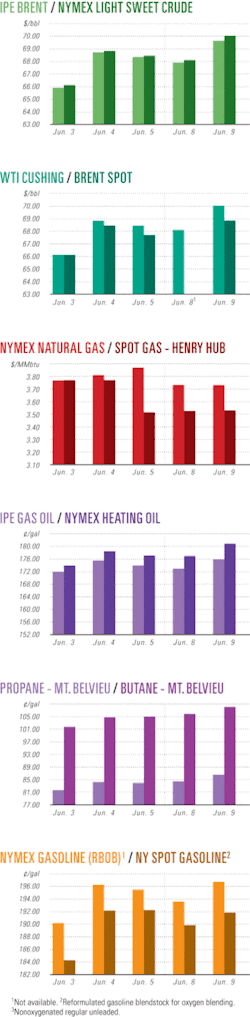
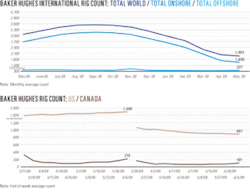
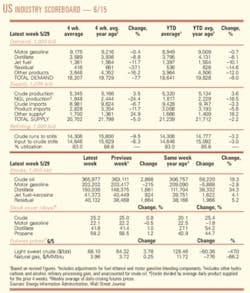
Industry Scoreboardnull
null
null
Exploration & Development Quick TakesExxonMobil finds oil in Brazil’s presalt layer
ExxonMobil Corp. has notified Brazil’s hydrocarbons regulator Agencia Nacional do Petroleo (ANP) that it has discovered oil on offshore Block BM-S-22 in the presalt layer of the Santos basin.
Traces of oil were found in a well drilled on the block, according to ExxonMobil, operator, which holds a 40% stake, while Hess Corp. holds 40% and Petroleo Brasileiro SA (Petrobras) 20%.
In November, David Rosenthal, vice-president, investor relations, said in a conference call that the West Polaris deepwater rig arrived in Brazilian waters in late September 2008 and began drilling the Azulao well on Block BM-S-22. He said ExxonMobil chartered the rig for 3 years and expected to have its first results on BM-S-22 by yearend 2008 or early 2009.
“Plans to drill a second well on the block are under way and will follow immediately upon completion of the first well,” Rosenthal said, confirming earlier reports that the firm would drill two wells at the site.
The ExxonMobil discovery follows one by Repsol YPF SA, which last week said it discovered hydrocarbons on Block BM-S-48 in the Santos basin, 185 km off Sao Paulo state (OGJ Online, Jan. 15, 2009).
Shelf’s Flatrock at 200 MMcfd and growing
Flatrock field in the Gulf of Mexico shelf is producing 200 MMcfd of gas from four wells, has more than 350 bcf of proved reserves by independent estimate, and has the potential to grow, said McMoRan Exploration Co., New Orleans.
Individual well rates vary depending on porosity, permeability, pressures, and hydrocarbon column, but the primary Miocene Rob-L reservoir has achieved the highest output at more than 100 MMcfd.
The No. 4 well, which tested at 124 MMcfd in October 2008, is making 60 MMcfd with a targeted gross rate of 90 MMcfd. The field’s Operc section is producing in two wells and being completed in a third well, and the No. 6 well might penetrate the upper Gyro section sands.
The No. 5 development well logged 155 net ft of Rob-L and Operc pay, is being completed in Operc, and is due on line in this year’s first quarter. The No. 6 delineation well on SMI 217 is drilling below 16,000 ft towards 19,700 ft. It logged 40 net ft of Rob-L pay.
The field was a July 2007 discovery in 10 ft of water on South Marsh Island Block 212.
Wintershall wins six Norwegian North Sea licenses
Wintershall will operate another five licenses in the Norwegian North Sea under Norway’s 2008 licensing round awards in predefined areas (APA).
The APA licensing rounds focus on mature areas of the Norwegian continental shelf. The government is keen to encourage development of smaller discoveries, which can be tied in to existing platforms and pipelines.
Norway’s energy ministry awarded 34 production licenses to 40 companies under the APA licensing round. It gave 21 licenses in the Norwegian North Sea, 11 licenses for the Norwegian Sea, and two for the Barents Sea off the coast of northern Norway.
Of the licenses awarded, Wintershall’s latest acquisition, Revus Energy ASA, received three, and Wintershall was awarded three, bringing its total award to six.
“The company is now one of the largest license holders on the Norwegian continental shelf and operates a total of 21 licenses,” said Harald Vabo, general manager of Wintershall Norge ASA. “We already plan to start with seismic activities on the new acreage in the next few months.”
PTTEP writes off Janaka-2 well off Myanmar
PTT Exploration & Production PLC’s recent probe for hydrocarbons in Myanmar’s Gulf of Martaban was a disappointment.
Although natural gas was found with Janaka-2, the first exploration well drilled on Block M3, the discovery was commercially insufficient, said the Thai state-controlled company.
Spudded on Sept. 28, 2008, the well was drilled to 3,351 m TD and encountered one 4-m petroleum-bearing formation.
The tubing stem test was not performed, and PTTEP wrote off $27.35 million, the cost of the well.
The results raised questions about the potential of the 7,770-sq-km acreage, especially as a previous well, Janaka-1 in PTTEP-operated Block M7, was abandoned earlier, although traces of gas were discovered (OGJ Online, Jan. 2, 2009).
However, PTTEP Chief Executive Anon Sirisaengtaksin vowed to continue studies on Block M3 and plans to evaluate the petroleum potential soon for additional exploration. Earlier last year, PTTEP acquired 500 line km of 2D seismic on M3.
PTTEP operates M3 and owns an 80% stake in it, with China National Offshore Oil Corp. holding the remaining 20% interest.
MGM to test Mackenzie Delta gas discovery
MGM Energy Corp., Calgary, plans in February to test a discovery on Ellice Island in northern Canada’s Mackenzie Delta that encountered four zones containing natural gas.
The deviated Ellice J-27 exploration well went to 2,102 m, 1,999 m true vertical depth, cut 57 m of gas-bearing sandstones in the four intervals. The company will test two of the zones and expects test rates to be sufficient to gain regulatory approval of a significant discovery license to encompass all prospective reservoirs.
MGM planned the well, first in this season’s three-well program, to test the Tertiary Lower Taglu and Aklak reservoirs in the footwall or southern part of the Ellice Island anticline.
MGM will move the Akita-Equitak 64 rig to the Ellice J-17 location where it expects to spud by Feb. 1. Ellice J-17 is planned to test a stratigraphic play on the west side of Langley Island.
The well locations are 80 miles northwest of Inuvik, NWT.
Nippon Oil farms into four PNG oil, gas fields
Nippon Oil Corp. subsidiary Nippon Oil Exploration Ltd. has acquired from Oil Search Ltd. (OSL) percentages in four exploration licenses for potential natural gas and oil fields in Papua New Guinea.
The Nippon unit, which will hold a 10% or 20% interest in each of the four licenses, hopes to begin joint exploration with OSL in 2009-11. It believes production at some of the fields could begin as early as 2010.
The farm-out agreements with OSL relate to the four exploration licenses: 20% of PPL219 and PPL239, both onshore; 20% of PPL234, offshore; and 10% of PPL244, offshore.
Analyst Global Insight said the farmouts will help OSL “monetize some of its assets and reduce its expenditure commitments in the fields, allowing the company to direct more capital towards a planned exploratory drilling program due to commence in late 2009.”
Nippon’s purchase is its second investment in Papua New Guinea since December when its affiliate, Merlin Petroleum Co., paid $800 million to AGL Energy Ltd. to triple its interest in a proposed $10 billion LNG project, led by ExxonMobil Corp., to 5.4% from 1.8% (OGJ Online, Dec. 20, 2008).
The fields to be explored by Nippon Oil Exploration and OSL could help generate feedstock for the proposed LNG facility, which is to be constructed near Port Moresby.
The facility, the first for Papua New Guinea, is expected to export 6.3 million tonnes/year of LNG starting in third-quarter 2013 (OGJ Online, Dec. 18, 2008). Sales negotiations with Japanese utilities are said to be under way.
The December agreement with AGL Energy also increased Nippon Oil’s interest in two central PNG producing oil fields, increasing the Japanese firm’s share of output to 8,000 b/d from its earlier 2,000 b/d.
Late last year, parent Nippon Oil and Nippon Mining Holdings Inc., faced with sluggish demand for gasoline in Japan, announced plans to merge their operations under a single holding company to be established in October 2009 (OGJ Online, Dec. 5, 2008).
Drilling & Production Quick TakesStatoilHydro prepares Gudrun field development
StatoilHydro plans to develop Gudrun oil and gas field in the Norwegian Sea using a fixed platform with seven production wells tied back to existing facilities in the Sleipner area and the Karsto processing plant north of Stavanger.
The company and its partners are designing the platform that will incorporate a subsea system in Sigrun field connecting to the future Gudrun platform. Later this year, the consortium will make a final decision on the development concept.
Gudrun lies 55 km north of Sleipner in 110 m of water. The high-pressure field has estimated reserves of 150 million boe.
The field was proved in 1974, and StatoilHydro became operator in 1997. “New technology, more information about the area, and the existing infrastructure have led to the field development now being realized,” the company said.
StatoilHydro has a 46.8% interest in the license. Marathon Norge holds 28.2%, and GDF Suez E&P Norge has 25%.
The Sleipner area contains Sleipner East and Sleipner West gas and condensate fields as well as satellite fields Gungne, Loke, and Alpha North.
BP awards Angolan subsea equipment contract
BP PLC and Sonangol Sinopec Ltd. have let a $140 million contract to FMC Technologies Inc. to manufacture and supply subsea equipment for Block 18 off Angola. Deliveries will start this year.
FMC will provide one gas export regulation manifold, foundations and controls, a high-integrity pressure protection system, chokes, and two pipeline end manifolds. The equipment will be manufactured in Angola and at FMC’s Kongsberg, Norway, facility.
The Greater Plutonio development on Block 18, BP’s first operated project in Angola, came on stream in 2007. It consists of 43 wells: 20 producers, 20 water injectors, and 3 gas injectors.
Petrobras cancels Papa-Terra platform bid process
Petroleo Brasilerio SA (Petrobras), citing uncertain market conditions, suspended the tenders for building the P-61 tension-leg well platform and P-63 floating production, storage, and offloading vessel for the Papa-Terra field, which lies in the Campos basin off Brazil.
The company noted that proposals received had an excessive cost.
Petrobras had expected the Papa-Terra field, discovered in 2003, to go on stream in 2011.
The company has formed an internal working group to analyze alternatives for developing the field that holds an estimated 700 million bbl of 14-17° gravity oil. Water depth is about 1,200 m.
Chevron Overseas of Brazil Ltd. is a partner in the field and holds a 37.5% interest.
BP lets $100 million subsea production contract
BP PLC has ordered engineering and project management services and subsea production systems valued at $100 million from Cameron for tieback projects and other operations in the Gulf of Mexico.
The equipment includes four subsea trees, production control systems, a manifold, flowline connection systems, and related equipment.
“Engineering work and procurement of materials began in the second quarter of 2008, and [equipment] deliveries are scheduled to begin in the fourth quarter of 2009 and continue throughout 2010,” Cameron said.
This is the first in a series of orders to be placed under a 2006 Gulf of Mexico framework agreement with BP, reflecting their joint standardization and engineering effort over the past 2 years.
Processing Quick TakesPemex delays refinery construction to yearend
Mexico’s Petroleos Mexicanos will delay construction of a refinery until yearend while the state firm studies the best location for the plant.
Pemex Chief Executive Officer Jesus Reyes Heroles said the 300,000 b/d refinery will cost $9-10 billion to build, but he noted that costs could fall due to reduced demand for services and equipment.
Pemex announced the refinery plan in mid-2008, and planned to begin preparing the refinery site before yearend 2008.
The company is eyeing nine possible sites for the proposed facility, including Cadereyta, Campeche, Dos Bocas, La Cangrejera, Lazaro Cardenas, Manzanillo, Salina Cruz, Tula and Tuxpan.
Governors of 15 states have been lobbying Pemex to make the investment in their states. The most recent is Tlaxcala state governor Hector Ortiz, who met with Heroles regarding the proposed new refinery, and presented a feasibility study to site the facility in his state.
Last October, President Felipe Calderon said his government would use 12 billion pesos ($853 million) from the country’s stabilization fund for investment in Pemex to begin building a new refinery in 2009, the first in nearly 30 years.
Increased refining capacity is considered urgent, as the country has spent almost $12 billion on petroleum product imports in 2000-07 due to a shortage of refining capacity, Pemex said.
Transportation Quick TakesFERC OKs Sparrows Point LNG terminal, line
The US Federal Energy Regulatory Commission has approved, with conditions, an LNG import terminal and connecting interstate pipeline proposed by AES Sparrows Point LNG LLC and Mid-Atlantic Express LLC. If built, the terminal will bring 1.5 bcfd to the US Northeast. FERC will impose 169 mitigation conditions, incorporating all mitigation conditions recommended by FERC’s environmental staff in the December 2008 final environmental impact statement.
Staff concluded that the Sparrows Point LNG terminal and pipeline project, with appropriate recommended mitigating measures, would have mostly limited adverse environmental impacts. FERC’s staff said in the final EIS that the US Coast Guard’s waterway suitability report for the project has “preliminarily determined” that additional recommended mitigation measures would be needed to make the Patapsco River, Chesapeake Bay, and territorial seas suitable for LNG marine traffic to the proposed terminal site and responsibly manage marine and safety risks (OGJ, Dec, 15, 2008, p. 22).
FERC also adopted the staff’s recommended pipeline route variations, addressing conflicts in congested areas through the northern portion of the pipeline route in Pennsylvania where significant residential growth had occurred. FERC will require site-specific residential plans for about 160 residences located within 50 ft of the construction site.
AES plans to construct and operate the import terminal and related facilities at an industrial port setting at Sparrows Point, southeast of Baltimore in Baltimore County, Maryland. Sparrows Point will increase the number of ships transiting as commercial marine traffic in Chesapeake Bay by 5-7%.
The project includes facilities capable of unloading LNG ships, storing up to 480,000 cu m of LNG, vaporizing the LNG, and sending out natural gas at a base-load rate of 1.5 bcfd.
FERC also authorized Mid-Atlantic Express to construct and operate an estimated 88 miles of 30-in. OD natural gas pipeline, 48 miles of which would be in Baltimore, Harford, and Cecil counties, Maryland, with the other 40 miles in Lancaster and Chester counties, Pennsylvania, ending in Eagle, Pa.
Inpex awards contract for Ichthys LNG plant
Japanese company Inpex Australia and its JV partner Total SA have awarded the front-end engineering and design contract for their proposed Ichthys LNG plant in Darwin to a consortium of JGC Corp., Chiyoda Corp., and Kellog Brown & Root—collectively known as JKC joint venture.
The FEED services, which will be carried out during 2009, mark a key milestone in the $20 billion (Aus.) Ichthys project. Gas from Ichthys field, in the Browse basin off Western Australia, will be piped 800 km to the LNG plant planned for Blaydin Point in Darwin Harbour in the Northern Territory.
The two-train project is expected to begin with production of 8 million tonnes/year of LNG along with 1.6 million tonnes/year of liquid petroleum gas and 100,000 b/d of condensate.
The first LNG shipments are scheduled for late 2014 or early 2015.
Operator Inpex says it remains firmly committed to the project despite the current global financial environment.
A separate FEED contract will be awarded for the offshore facilities shortly, Inpex said.
Woodside shelves OceanWay LNG terminal
Woodside Petroleum Ltd., Perth, has suspended its proposed OceanWay LNG import terminal off the Californian coast near Los Angeles just over a month after saying it was continuing the project, but at reduced size.
Woodside still believes in the long-term value of LNG as a source of clean, reliable energy for Los Angeles, according to Steve Larson, Woodside natural gas president. However, Larson said the impact of the current market conditions had led to a withdrawal of the application to Californian authorities “for the time being.” The decision was taken in the face of rising US domestic gas production and lower gas prices.
The regulatory authorities have been notified.
In December 2008 Woodside reduced the number of regasification tankers for the project from two to one, citing community and regulatory concerns as well as a perceived fall in customer demand.
The plan involved bringing LNG from Woodside’s Australian gas projects, converting the LNG back to natural gas in regasification tankers and unloading the gas through underwater buoys 45 km off Los Angeles. The gas was to be piped into the southern Californian network via a hub at Los Angeles International Airport.
Larson said the permitting process in California was challenging, but Woodside had been confident that its design was safe and environmentally sound and would ultimately have succeeded.
Australian analysts say withdrawal from the project is not particularly significant for Woodside and is unlikely to have much impact on the company’s share valuation or its planned workload in Australia.