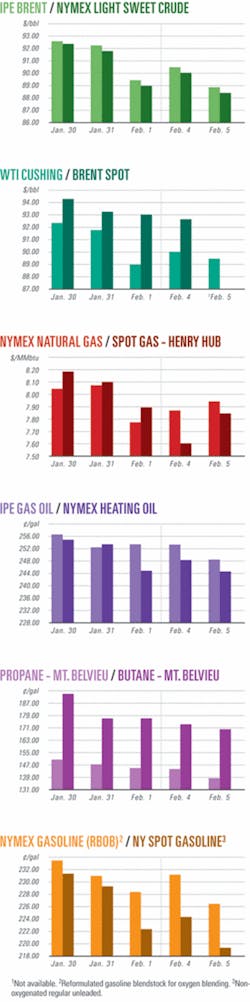
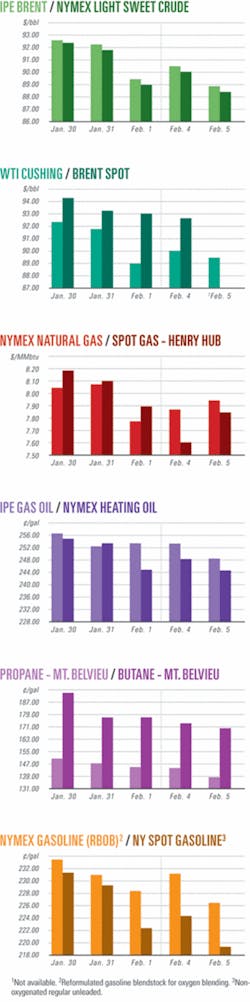
OGJ Newsletter
Enbridge to lead industry CCS project
Enbridge Inc. plans to lead a group of 19 oil companies and electric utilities in the Alberta Saline Aquifer Project (ASAP), a carbon capture and storage (CCS) research and pilot sequestration project.
Other companies involved include BP Canada Energy Co., Chevron Canada Resources, ConocoPhillips, EnCana Corp., Penn West Energy Trust, and TransCanada.
Initially, ASAP will identify deep saline aquifers suitable for long-term storage of carbon dioxide in Canada. The first phase is expected to be completed by yearend.
A second phase calls for designing sequestration sites to receive injected carbon dioxide. Later phases could involve large-scale, long-term commercial sequestration.
On Feb. 1, a joint federal-provincial government panel recommended that Canadian governments invest $2 billion (Can.), to be matched by energy industry funding, toward CCS research with the goal of sequestering 5 million tonnes of carbon dioxide by 2015.
Finance minister lauds French industry fuel prices
In an unprecedented move, French Finance and Economy Minister Christine Lagarde commended oil companies and distributors for keeping a promise made at the Nov. 10, 2007, roundtable she chaired, that they would address oil price peaks and pass along price drops as quickly as possible at service stations.
She noted in a press release that the price of motor fuels had returned in late January to the preround table level following heights reached in early January. She said three factors explained variations in the price of motor fuels over the last few weeks in France, pushing up prices:
- The impact of the French biofuels plan, which since Jan.1 has jumped to a 5.75% incorporation into motor fuels. That goal was set by the European Union for 2010, but France anticipated it earlier, leading to logistic adaptations and costlier supply.
- The turnaround of a number of refineries, the reduction in product sulfur content, and the railway strikes that resulted in higher costs in late November.
- The increase in the internal oil products tax, which the government had transferred to the regions.
Jean-Louis Schilansky, delegate general of the oil companies’ trade group UFIP, told OGJ that the price of gasoline and diesel fuel increased by some €0.02/l. compared with what it should have been.
Schilansky said, “What we really appreciate is the rational analysis of the situation by the government. The price of motor fuels is now being discussed at an economic level and no longer in a political and polemical way.”
Japan, S. Korea retain global LNG import lead
Japan remained the world’s largest LNG importer in 2007, at 65.7 million tonnes of LNG, up 5.7% over 2006, according to Pan EurAsian Enterprises. South Korea remained the world’s second largest LNG importer at 25.6 million tonnes, up 1.2% over 2006.
Pan EurAsian cited the next six largest global LNG importers in 2007, in millions of tonnes of LNG, as: Spain 19.1; US 17; France 10.2; Taiwan 8.3; India 6.2; and Turkey (with only one terminal) 3.5.
Taiwan’s LNG imports were up 6.8% over 2006, Pan EurAsian reported, and China appeared in the reckoningwith imports of 2.9 million tonnes, up from less than 10% of that amount in 2006.
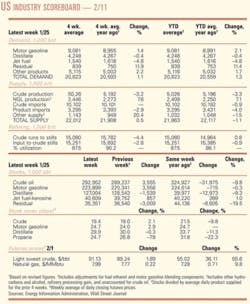
Industry Scoreboardnull
null
null
Exploration & Development - Quick TakesChukchi Sea sale draws $2.66 billion in high bids
Oil and gas producers submitted $2.66 billion in apparent high bids in a record-breaking offshore federal lease sale in Alaska, the US Minerals Management Service said Feb. 6.
The 677 bids on 488 blocks in the first Chukchi Sea lease sale since 1991 made it the most successful Outer Continental Shelf lease sale in Alaska’s history, MMS said. Shell Gulf of Mexico Inc. submitted the single largest bidmore than $105.3 million. Shell also led in total bids, with 302 totaling nearly $2.2 billion, 275 of them high bids for nearly $2.12 billion.
ConocoPhillips was the second most active bidder, submitting 145 bids for $1.1 billion, including 98 high bids for more than $506.4 million. Other participants included Repsol E&P USA Inc. with 104 total bids for $15.6 million, 93 of which were high bids for more than $14.4 million and Eni Petroleum US Inc. with 74 total bids for nearly $35 million, 17 of which were high bids for nearly $8.9 million.
StatoilHydro USA E&P Inc., Iona Energy Co. (US) Ltd., and North American Civil Recoveries Arbitrage Corp. also submitted high bids, according to MMS.
The US Department of Interior agency received nearly $3.39 billion in bids from the seven companies for 2,304-acre tracts spread over more than 29 million acres. It said that each high bid now will be evaluated to assure that it represents a fair market value before a lease is issued. The closest awarded tract to land is 54 miles offshore, MMS said.
The sale took place despite protests that oil and gas activity could pose a threat to polar bears, which another DOI agency, the US Fish and Wildlife Service, is considering listing as an endangered species. Interior Secretary Dirk A. Kempthorne and other DOI officials have said that the threat comes from melting sea ice and that the bears already have strong safeguards under the Marine Mammal Protection Act. Lease terms will include stringent environmental provisions, MMS Director Randall L. Luthi noted.
Oil industry and other groups expressed their support for the sale on Feb. 6. The American Petroleum Institute called it “a welcome first step toward increasing much-needed energy supplies for US consumers and the US economy.”
Meanwhile, National Association of Manufacturers Pres. John Engler said production from the Chukchi Sea would reduce US dependence on foreign sources.
The US Oil & Gas Association said the area’s oil and gas resources represent an important domestic energy opportunity that should not be ignored.
Shell makes oil find at Vicksburg in eastern gulf
Shell Oil Co. has made an oil discovery at the Vicksburg prospect in 7,500 ft of water on DeSoto Canyon Blocks 353 and 397 and Mississippi Canyon Block 393, in the eastern Gulf of Mexico.
The well was drilled to a depth of 25,400 ft and found a 300-ft hydrocarbon column. Transocean’s semisubmersible Deepwater Nautilus, on contract to Shell, drilled the well.
Shell is operator of Vicksburg with a 57.5% interest. Vicksburg partners are Nexen Inc. 25% and Plains Exploration & Production Co. 17.5%.
BP has 15th oil discovery on Block 31 off Angola
Sonangol EP and BP Exploration (Angola) Ltd., operator, have reported the Portia oil discovery on ultradeepwater Block 31, off Angola. Well test results confirmed the capacity of the reservoir to flow more than 5,000 b/d under production conditions, BP said.
The well lies 7 km north of the Titania discovery and 10.5 km southwest of Plutao field. Portia is the 15th discovery BP has drilled on Block 31. Portia was drilled in 2,012 m of water 386 km northwest of Luanda. It reached 5,678 m TVD subsea. This is the fourth discovery on Block 31 in which the exploration well was drilled through salt to access an oil-bearing sandstone reservoir beneath.
Although oil deposits are commonly associated with salt, salt distorts seismic images, so salt-affected areas require additional seismic processing and interpretation prior to drilling.
Sonangol is the concessionaire of Block 31, which covers 5,349 sq km and lies in 1,500-2,500 m of water. BP holds 26.67%. Other interest owners are Esso Exploration & Production Angola (Block 31) Ltd. 25%, Sonangol 20%, Statoil Angola AS 13.33%, Marathon International Petroleum Angola Block 31 Ltd. 10%, and Total Group subsidiary Tepa Block 31 Ltd. 5%.
Chevron completes Big Foot in deepwater gulf
Chevron Corp. reported the successful completion of an appraisal well at its Big Foot prospect in the deepwater Gulf of Mexico. Big Foot lies in more than 5,000 ft of water on Walker Ridge Block 29, about 225 miles south of New Orleans and 180 miles offshore.
The appraisal well, Big Foot No. 3, Sidetrack No. 2, confirmed the same pay intervals of the previously announced discovery and sidetrack wells, and found the main pay sand full of oil to the base, Chevron said.
Operated by a Chevron subsidiary, the appraisal well reached a measured depth of 25,113 ft (including water) to the northwest of, and deeper than, the previous wells. Chevron is evaluating a range of production development options for the Big Foot prospect.
Chevron owns a 60% working interest in Big Foot. Partners are StatoilHydro AS 27.5% and Shell Gulf of Mexico Inc. 12.5%.
Drilling & Production - Quick TakesPDVSA pays Total, StatoilHydro for Orinoco items
Venezuela will pay $1.1 billion in compensation to StatoilHydro AS and France’s Total SA for its nationalization of an oil project they previously controlled.
State-owned Petroleos de Venezuela SA (PDVSA) agreed to pay its partners for their reduced stakes in the Sincor heavy oil venture with a combination of crude oil and cash.
However, Total and StatoilHydro must pay some $130 million of their compensation as a “bonus” to fund the new Sincor joint venture company.
After that deduction, Total will receive $735 million in the form of quarterly crude oil shipments, while Statoil will receive $235 million in cash.
President Hugo Chavez’s government last May took over majority stakes in heavy oil upgrading projects located along the Orinoco River basin operated by four international oil companies.
While StatoilHydro and Total agreed to remain as minority partners under new arrangements with the government, ConocoPhillips and ExxonMobil Corp. declined to accept the government offer.
PDVSA has not announced any results of its compensation talks with the two US firms, but reports suggest that the Venezuelan firm is exploring all forms of compensation including payment in crude.
Meanwhile, StatoilHydro signed an agreement with Venezuela to quantify the reserves of the Junin 10 block in the Orinoco belt with a view to developing them.
A local StatoilHydro official said the firm sees enormous reserves potential in the country.
Chavez wants the Orinoco belt reserves certification process completed by 2010. He hopes that certification will boost his country’s reserves to more than 300 billion bbl from the current 100 billion bbl.
Regardless of the amount of reserves, however, Orinoco oil will be a boost to the country’s output potential and earnings.
Falling outside of the quota system of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries, to which Venezuela belongs, Orinoco’s heavy oil reserves would enable Chavez to ramp up production and sales without the need for any authorization from OPEC.
BPZ Energy-chartered tanker sinks off Peru
A Peruvian Navy tanker chartered by BPZ Energy Inc. of Houston caught fire and sank on Jan. 30. The tanker, Supe, which was moored near the Corvina CX-11 platform in Corvina field off Peru, was being used for oil storage.
At the time of the accident, it held 1,300 bbl of oil, most of which is believed to have burned in the fire. The tanker had a capacity of 7,500 bbl.
“Initial assessments show that environmental issues have been adequately controlled,” BPZ said. A full investigation is under way, the company said.
The Supe tanker sank about 1½ miles from the platform, which started production Nov. 1, 2007 (OGJ, Dec. 10, 2007, p. 22).
The tanker stored oil produced from the 21XD and 14D wells. Current production, 4,200 b/d of oil, and the testing operations on the 18XD well were temporarily suspended.
Initial reported indicated no damage to the platform, barges, drilling, and well-testing equipment.
BPZ said damage appears to have been limited mostly to the tanker, which was moved farther away from the platform after catching fire.
Twelve Peruvian Navy sailors working aboard the tanker were injured and evacuated to area hospitals. Two sailors were treated and released while 10 sailors were evacuated to Lima via a Peruvian Navy hospital plane.
Processing - Quick TakesSinopec, Sabic plan petrochemical plant in China
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) and Saudi Basic Industries Corp. (Sabic) have signed a nonbinding document outlining the main issues for a tentative 50-50 joint venture to build a $1.7 billion ethylene derivatives complex in Tianjin, China.
The proposed complex would produce 1 million tonnes/year of ethylene derivatives600,000 tonnes/year of polyethylene and 400,000 tonnes/year of ethylene glycoland is proposed to be completed by September 2009. All of its ethylene feedstock would be supplied by Tianjin Petrochemical Co., a branch of Sinopec.
This would be Sabic’s first JV in China. Company officials said China is an important market for Sabic, which hopes to become one of the world’s top petrochemical companies by 2020.
Petroecuador, PDVSA plan refinery in Ecuador
Ecuador and Venezuela plan to jointly finance and build a 300,000 b/d refinery in Ecuador’s coastal province of Manabi, according to Ecuador’s Mines and Oil Ministry.
The ministry said representatives of state oil companies Petroecuador of Ecuador and PDVSA of Venezuela met in Quito, Ecuador, to discuss project details.
“The group analyzed the legal aspects to constitute the mixed economies enterprise and drafted the schedule for preparing the documents,” to ensure that the representatives of both companies could sign the contract in March, the ministry said.
Plans call for the completion of a feasibility study for the project in June, with construction to be completed within 4 years. No date for the start of construction was provided.
Ecuador’s oil minister Galo Chiriboga Zambrano said the refinery will be financed equally by the two countries and supplied largely with crude from Ecuador. “But later on, it would (use) Venezuelan oil when ours is depleted,” the minister said.
Sinopec to upgrade Changling, Baling refineries
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) will invest about $2.2 billion to raise the production capacity of two domestic refineries.
The announcement came as Chinese officials, who have pledged a better system of supply, scrambled to meet growing domestic demand in the face of a particularly cold winter.
Sinopec will spend about $1.4 billion in expanding its Changling refinery in central China’s Hunan province, by doubling its production capacity to 10 million tonnes/year.
It will spend an additional $834.3 million to upgrade its Baling plant, which processes oil from Changling into chemicals.
The move follows the central government’s pledge to meet rising domestic fuel demand. The Chinese state-owned refiners are required to ensure the supply after transportation systems in many provinces were disrupted by the snowstorms.
The upgrade announcement came as Chinese officials struggled to cope with their country’s worst winter storms in decades.
The China Meteorological Administration said the bad weather, including more snow, was expected to continue for at least the next 3 days in parts of eastern and southern China.
“Guizhou, Jiangsu, and Shandong have suffered their worst snowfalls in 50 years,” the administration said. For Hunan and Shaanxi provinces, it was the worst in 20 years.
Sinopec’s upgrade also coincided with reports that China reached new highs for oil production, imports, and consumption in 2007.
In 2007 China produced 186.7 million tonnes of crude, up 1.6% from 2006, while its net oil imports were 159.28 million tonnes, up 14.7%.
The country’s oil consumption, representing the sum of net imports plus output, rose 7.3% to 346 million tonnes in 2007, meaning that that imports account for about 46% of China’s oil consumption.
China refined 326.79 million tonnes of crude in 2007, representing a growth of 6.4%about the same as the 6.3% recorded in 2006.
The output of refined oil products, comprised of gasoline, diesel, and kerosine, stood at 195 million tonnes, up 7.2% year-on-year or about 2.5% higher than in 2006.
Officials said that the diesel shortage that occurred in the country in second half 2007 led to an especially sharp rise in diesel imports, rising by 130.1% to 1.62 million tonnes, while diesel exports fell by 14.9% to 660,000 tonnes.
Transportation - Quick TakesBechtel to build Angola’s first LNG plant
Angola LNG Ltd. is planning Angola’s first gas liquefaction facility near Soyo in Zaire Province. The LNG plant will have a nominal capacity of 5.2 million tonnes/year of LNG and will include storage for LNG, LPG, and condensate; and a loading jetty sized to accommodate ships as large as 210,000 cu m. A subsidiary of the Bechtel group will construct the plant.
The project is an integrated gas utilization project encompassing offshore and onshore operations monetizing gas from blocks off Angola. First LNG from the project is expected by early 2012 (OGJ, Jan. 7, 2008, p. 21).
Angola LNG Ltd. has licensed ConocoPhillips’s proprietary natural gas liquefaction technology. “The Bechtel-ConocoPhillips proposal was selected as the successful bid following a comprehensive evaluation of two competitive proposals submitted following the front-end engineering design (FEED) competition for the LNG facility,” said Ken Marrs, Angola LNG Ltd. project manager.
Angola LNG Ltd. shareholders are affiliates of Sonangol 22.8%, Chevron Corp. 36.4%, BP PLC 13.6%, Total SA 13.6%, and Eni SPA 13.6%.
Singapore to build LNG terminal by early 2009
Construction of a planned $1 billion LNG regasification terminal in Singapore is expected to begin by late this year or early 2009 to enable the city-state to begin importing LNG by late 2011-early 2012, according to a senior official (OGJ, Oct. 1, 2007, Newsletter).
S. Iswaran, Minister of State for Trade and Industry, said Singapore needs to move forward with LNG as an important part of its policy to diversify energy sources. Currently, Singapore depends on natural gas piped in from neighboring Malaysia and Indonesia.
Iswaran said PowerGas, the wholly owned subsidiary of Singapore Power, has made good progress toward the construction start and should be able to make some critical decisions shortly.
PowerGas has been identifying core capabilities needed for the expansion, Iswaran added, and they are assessing partnerships to enhance expertise within the consortia in order to develop the terminal. “After selecting partners and completing the complex design process...they will need to start actual work by the end of this year or early next year,” to meet the import target, he said.
Iswaran’s remarks came after an announcement by the country’s Energy Market Authority that it had short-listed five groups competing to be the sole LNG importer-consortium from a total of 18 proposals involving 22 companies. EMA did not disclose their identities due to requests for confidentiality. Selection is slated for the second quarter.
The market response was promising, Iswaran said, and Singapore had “very strong” proposals from the diverse organizations.
W. Australia assesses common-use LNG hub
Western Australia and Australia’s new Kevin Rudd-led federal government have agreed to assess the Kimberley region of Western Australia as a site for a common-user LNG hub and associated regional activities to serve proposed gas fields to be developed in the offshore Browse basin.
Their aim is to prevent piecemeal development following an environmentalist outcry in 2007 at proposals by Woodside Petroleum, Inpex, and others to establish LNG plants at several locations on the Kimberley coast or on offshore islands. The region is regarded as a pristine wilderness, and public opinion is that it should be kept that way.
Industry sources appear relatively comfortable with the government initiative as long as the companies concerned are involved in the consultation process.
The Australian Petroleum Production & Exploration Association said the industry would like a list of potential sites by mid-2008 and a final decision by yearend. APPEA does not want to see the process stalled by “green politics.”
The companies involved are aware of the pristine nature of the environment but know that differing distances of the offshore gas fields from the coast will mean that each company will prefer different sites. None wants to see a competitive advantage given to another. The single hub plan also raises the question of potentially massive public infrastructure investment to ensure that facilities such as ports, roads, and other access resources remain available to all users.
The single hub proposal will build on work already performed by Western Australia’s Northern Development Taskforce, which has been attempting to achieve a balance between Browse basin development and environmental and heritage interests.
NNPC sets up shipping firm for Nigerian LNG
Nigerian National Petroleum Corp. has established a new shipping company, Nikorma Shipping Services Ltd., to handle the additional volume of Nigerian LNG exports expected in the coming years.
NNPC, which has taken a 51% holding in the venture, plans to reduce this to 30%, offering the remaining shares to private Nigerian investors.
NNPC established Nikorma Shipping with shareholder participation from MISC Bhd., Hyundai Heavy Industries Co. Ltd., and local shipping and logistics firm Deepwater Shipping & Maritime Co. Ltd. MISC will have a 30% holding, HHI 11.5%, and DSMC 7.5%.
Nigeria’s LNG exports are projected to rise to 60 million tonnes/year from a current level of 17.9 million tonnes/year over the next 5 years.
Enbridge’s N. Dakota line expansion in service
Enbridge Energy Partners LP has begun service on its recently completed Phase 5 oil transmission system expansion in North Dakota that increased the system’s capacity to 110,000 b/d.
The $78 million project added 30,000 b/d of capacity, with 52 miles of loop on the existing gathering system, 10 new or upgraded pump stations, and additional tankage.
An additional 51,000 b/d of capacity is planned in Phase 6, which would bring total system capacity to 161,000 b/d by early 2010.