Vector Pipeline costs run past estimates
Vector Pipeline LP is a partnership of Enbridge Inc., Calgary, Westcoast Energy Inc., Vancouver, and MCN Energy Group Inc., Detroit.
The system began operations Dec. 1, 2000, moving western Canadian and US-sourced natural gas from the market hub in Chicago to the hub at Dawn, Ont. It also provides access to markets and storage in the upper US Midwest.
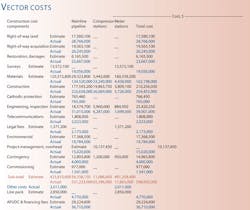
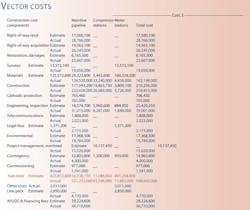
The company filed a cost comparison for the 269 mile, 42-in. US portion of the line earlier this year (table). That filing provides a window onto what such a project can encounter during construction.
Major areas
The company explained the major cost variances under three general headings: weather effects, land access, and urbanization.
Construction cost estimates of $523,333,000, part of an amended certificate filed with FERC in June 2000 before construction start-up in summer 2000, assumed normal summer weather. In fact, summer 2000 in the upper Midwest US was abnormally wet.
The company said May was the ninth wettest month in 106 years of records in Illinois. Heavy rainfall continued in June, making it the sixth wettest month on record, and Illinois received the third highest rainfall in the 106-year period.
The extensive rains reduced productivity, said the company, and working through these periods resulted in higher costs because of the wet and muddy conditions.
The high rainfall also raised the groundwater table, which created new areas requiring wetland construction techniques and extended existing ones. Construction temporarily bypassed unworkable sections, leading to unavoidable inefficiencies and cost increases.
Vector also said it encountered significant difficulties and delays with land access. Among these, extended legal challenges from some landowners over access for survey and construction and compensation issues created locations where the necessary access was unavailable when required.
More inefficiencies ensued from lack of timely access. The landowner challenges resulted in higher than anticipated compensation along with significant increases in related legal and survey costs.
Finally, Vector failed to anticipate fully the amount of urbanization along its route. The increased density resulted in crowded workspace that increased the need for additional workspace and affected construction.
Examples of significant increases over originally estimated costs include:
- Cost of land and ROW increased by 64%.
- Costs for negotiating and litigating ROW easements increased by 34%.
- Costs for restoration and damages increased by 280%.
- Costs for surveying the route and temporary workspaces increased by about 40%.
- Construction costs increased by about 26%.
- Engineering and inspection costs increased about 53%.
- Legal feels increased by 58%.
- Costs for environmental analysis and evaluation increased by 14%.
- Project management costs increased by 48%.
- Commissioning costs increased by 58%.