General Interest - Quick Takes
Brazil sees oil self-sufficiency next year
Brazil expects to achieve oil self-sufficiency next year by producing nearly 2 million b/d of oil, Finance Minister Silas Rondeau said.
Currently, Brazil produces 1.73 million b/d of oil and projects yearend consumption of 1.85 million b/d. “Self-sufficiency in petroleum should be reached...in 2006,” Rondeau said.
Guilherme Estrella, Petrobras’s exploration and production director, said that during 2006-10 Petrobras plans to invest $34.1 billion in exploration and production. The company will spend $28 billion in Brazil, including $4.1 billion on exploration and $23.9 billion on production and development, he said.
During the 1970s, Brazil imported 85% of the oil it consumed, causing a financial crisis that lasted more than a decade.
Its commitment to exploration and production includes a new emphasis on natural gas. “We estimate that in 10 years we’ll have 70 million cu m/day of gas-about four times what we have now,” Rondeau said. He also said it’s too early to project when Brazil might reach self-sufficiency in gas.
Weyburn project illustrates CO2 sequestration
Five million tons of carbon dioxide were successfully sequestered in Weyburn oil field in Saskatchewan while the field’s oil recovery rate doubled, the US Department of Energy reported. DOE helped fund the project.
If successfully applied worldwide, the methodology could eliminate one third to one half of CO2 emissions associated with oil production in the next 100 years while recovering billions of additional barrels, DOE said.
“Just by applying this technique to the oil fields of Western Canada, we would see billions of additional barrels of oil and a reduction in CO2 emissions equivalent to pulling more than 200 million cars off the road for a year,” Energy Sec. Samuel W. Bodman said. The project is a multinational effort led by Canada’s Petroleum Technology Research Centre in Regina, Sask., and cosponsored by the oil field operator, EnCana Corp. of Calgary. Along with funding from DOE, the project receives funds from industry and government organizations in Canada, Japan, and the European Community.
In the project’s first phase, CO2 piped from the Great Plains synthetic fuels plant in Beulah, ND, was injected into Weyburn field to increase underground pressure and bring more oil to the surface.
Production was increased by 10,000 b/d as a result, DOE said.
The project also demonstrated permanent carbon sequestration’s technical and economic feasibility. Previously, much of the CO2 used in similar US EOR projects was taken from naturally occurring reservoirs at considerable cost. DOE said that using an industrial source sequesters CO2 emissions that normally would be vented into the atmosphere.
Scientists project that knowledge gained from the project will keep Weyburn oil field viable for an additional 20 years, produce an additional 130 million bbl of oil, and sequester as much as 30 million tons of CO2.
Canada’s NEB expects rise in CBM production
Canada’s National Energy Board expects that the total average Canadian gas production will increase to 17.3 bcfd by yearend 2007 from 16.9 bcfd in 2004.
In its report, Short-term Canadian Natural Gas Deliverability 2005-07, NEB discusses the short-term gas supply situation by examining recent production trends in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin and off eastern Canada.
NEB Chairman Ken Vollman said, “While production of conventional gas in the WCSB is expected to decline slightly, the increase in production of natural gas from [coalbed methane] is expected to offset the declines and enable a small increase in gas deliverability.” Regarding eastern Canada, NEB expects production from the Sable project off Nova Scotia will remain at 400 MMcfd of gas during 2005-06. The installation of compression facilities is expected to briefly boost production to 500 MMcfd during 2007.
Elsewhere on the Nova Scotia shelf, the industry has taken several costly hits as three wells came up dry last year (OGJ, Aug. 9, 2004, p. 44).
Meanwhile, rising natural gas prices have prompted record gas drilling levels across Canada. NEB anticipates that industry will maintain very high drilling levels, but the effort is expected to result in only a modest increase in total Canadian gas production during the next 2 years.
Almost 98% of Canadian gas production now comes from the WCSB, with Alberta accounting for 80% while British Columbia accounts for 16%, and Saskatchewan accounts for 4%.
NEB expects that WCSB conventional gas production will drop to 16 bcfd in 2007 from 16.3 bcfd in 2004.
Meanwhile, CBM production in the WCSB is growing rapidly. NEB projects CBM production there will reach 900 MMcfd by yearend 2007 compared with an estimated 300 MMcfd in 2005.
Warning issued on EU gas, power deregulation
The European Commission has warned members of the European Union to accelerate deregulation of their electricity and gas markets or face “stronger action.”
The EC adopted a report highlighting slow progress on compliance with deregulation directives and disclosed initial findings of a separate competition sector inquiry that it said confirmed the report findings.
“Member states need to quickly and fully implement the gas and electricity directives not only in letter but also in spirit,” said Energy Commissioner Andris Piebalgs, promising continued pressure on members to increase electricity and gas competition. “If this does not happen, stronger action will be needed.”
Competition Commissioner Neelie Kroes said the report shows “evidence of serious malfunctions” in EU energy competitiveness and warned, “I am determined to use competition law to protect European industry and consumers.”
The report said cross-border competition in gas and electricity hasn’t developed to the point that customers have real alternatives to nationally established energy suppliers. It cited the absence of price convergence across the EU and low cross-border trade.
It also said the gas market lacks liquidity of both gas supply and transport capacity. The competition sector inquiry paralleling the report began in June and includes responses from the energy industry and customers.
Among its findings:
• Gas and electricity markets in many EU member countries remain concentrated and allow existing operators to influence prices.
• Many wholesale markets are not liquid because of long-term contracts, in the case of gas, or because companies are active in both production and retail marketing, in the case of electricity. Unbundling of network and supply activities is inadequate.
• Barriers to cross-border supply of gas and electricity prevent development of integrated EU energy markets.
• Markets are insufficiently transparent.
• Industry and consumers have little trust in specific price formation mechanisms on energy wholesale markets. ✦
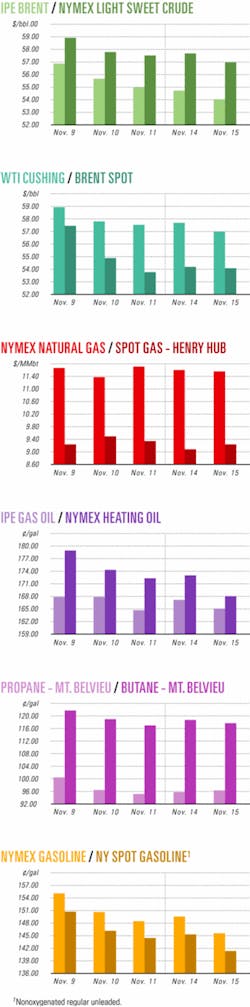
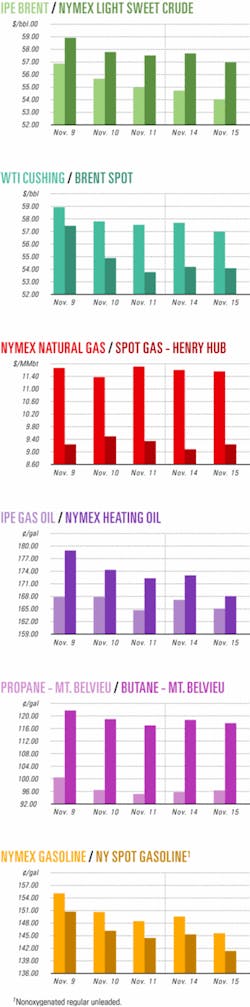
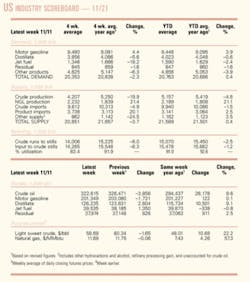
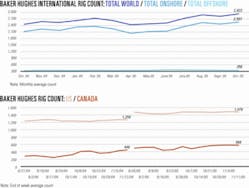
Industry Scoreboard
null
null
null
Exploration & Development - Quick Takes
India’s NELP VI likely format’s last round
India’s Dir. Gen. of Hydrocarbons V.K. Sibal confirmed at a meeting in New Delhi that the upcoming new exploration licensing policy (NELP) round would likely be the last as India moves toward a more-transparent open acreage nomination system.
Sibal told OGJ that NELP VI probably will commence in late January or early February 2006. NELP I began in January 1999.
NELP VI will offer about 50 blocks of mixed size equally distributed between onshore and offshore.
Sibal wants to attract a more diverse group of exploration companies and is therefore offering incentives for participation in smaller blocks.
“Previously, the blocks on offer were too large” to properly explore, Sibal said. They ranged in size from 500 sq km to 20,000-30,000 sq km.
Changes in the upcoming NELP VI from previous rounds include:
• Block sizes as small as 16 sq km.
• Phase 1 work commitment to include 2D seismic surveys but no minimum drilling commitment.
• Reapportioning phased work commitments to eliminate front-loading of costs.
• Designated coalbed methane acreage.
As in previous NELP rounds, India has not stipulated any up-front bonuses. A new opportunity for companies to nominate open acreage in India will be announced during NELP VI. Sibal said bidding on open acreage will likely begin in December 2006.
Petrobras drilling long-reach Serra well
Brazil’s state-owned Petroleo Brasileiro SA (Petrobras) has begun drilling an oil well in Serra field in the northern state of Rio Grande do Norte that will have the largest ratio between vertical depth and horizontal reach of any well in Brazil.
Petrobras 7-SER-17D will have a vertical depth of 950 m, a horizontal distance from the well of 2,800 m, and a total measured depth of 3,300 m. Queiroz Galvão’s QG-2 rig is drilling the well, which is expected to be completed in December.
The Serra campaign is being conducted carefully due to the environmental sensitivity of the region, said Petrobras officials. The well is being drilled from an onshore location to a target below 3 m of water.
Engineer Vicente Abel Soares Costa said Petrobras’s Rio Grande do Norte business unit is conducting an environmental program in Serra to ensure that drilling will not hurt the environment. Among the safeguards are the use of biodegradable fluids, gravel drying, the extraction and containment of generated liquid and solid wastes, and sanitary facilities at drilling locations. Serra field has 16 producing wells, of which 12 are long-reach types. The average production of each well is 100 cu m/day of 30° gravity oil.
Petrobras lets Roncador field development contract
Petrobras has awarded a consortium of Subsea 7 Inc. and Technip to supply and install the flexible lines that will connect 30 wells in the giant Roncador field in the Campos basin to the P-52 platform.
Subsea 7 selected Aker Kvaerner Subsea do Brasil to supply the connection systems, which are slated for delivery in November 2006. Flexible line installation work is expected to start in August 2006. The work will include the supply of two emergency shutdown valves, four pipeline end manifolds, and vertical connection modules.
Brigham expands into Williston Bakken play
Brigham Exploration Co., Austin, acquired a 100% working interest in 46,000 acres in the Mississippian Middle Bakken formation in northwestern North Dakota and could spud its first well late this year.
The acreage, for which Brigham paid $4.6 million, is 20-40 miles east of teeming Bakken horizontal drilling in Richland County, Mont. (OGJ Online, June 28, 2005).
Operators have completed 227 Bakken wells in 324 sq miles at which initial flow rates averaged 345 b/d of oil. Estimated ultimate recovery is 376,000 bbl/well, and cumulative production has averaged 112,000 bbl/well, Brigham said. The wells generally have 4,000-9,000-ft laterals at 11,000 ft TVD.
Outlays for drilling in so-called nonconventional plays could make up 25% of Brigham’s 2006 capital budget, the company said. ✦
Drilling & Production - Quick Takes
Husky begins production at White Rose field
Husky Energy Inc., Calgary, has begun production from White Rose oil field in the Jeanne d’Arc basin, 350 km east of St. John’s, Newf. The company said oil was introduced into the process stream of the SeaRose floating production, storage, and offloading vessel (FPSO) Nov. 12.
Husky has chartered two Samsung-designed, double-hulled shuttle tankers-the Heather Knutsen and the Jasmine Knutsen, each with 1 million bbl of crude capacity-to transport White Rose production. The Heather Knutsen tanker is scheduled to take delivery of the first shipment from the SeaRose FPSO in late November.
Husky, operator of the $2.35 billion White Rose project, anticipates peak production of 100,000 b/d of oil in first half 2006. It estimates the field’s probable reserves at 200-250 million bbl (OGJ Online, Aug. 12, 2004). Husky holds 72.5% interest in the field, and Petro-Canada, 27.5% (OGJ Online, Aug. 28, 2005).
Chevron reports start of Tahiti spar hull construction
France’s Technip has started cutting steel for construction of the spar hull and topsides modules of a floating production and mooring systems to be installed in the deepwater Tahiti field in the Gulf of Mexico (OGJ, Oct. 3, 2005, Newsletter).
Chevron Corp. said that steel was cut for the hull starting on Oct. 16 at a Technip yard in Pori, Finland. Steel was cut for the topsides modules starting on Oct. 18 at Technip subsidiary Gulf Marine Fabricators at its yard near Corpus Christi, Tex.
The deepwater spar hull will be 170 m long and 39 m in diameter and have a steel weight of 24,000 tonnes. It is slated for delivery to the Gulf of Mexico by mid-2007, with topsides fabrication expected to be completed at about the same time. Tahiti field lies on Green Canyon Blocks 596, 597, 640, and 641 in 4,200 ft of water about 190 miles southwest of New Orleans. The Tahiti facility will have the capacity to produce 125,000 b/d of oil and 70 MMscfd of gas and treat 120,000 b/d of produced water.
More Bohai Bay production brought on stream
CNOOC Ltd. announced initial production from the Caofeidian (CFD) 11-3/5 oil fields on western Bohai Bay Block 04/36. Using an unmanned facility, the fields are producing at 13,800 b/d of crude oil. The fields are in an average depth of 25 m of water. The development was combined with CFD 11-1 and CFD 11-2 to enhance the economics (OGJ, July 11, 2005, p. 35).
Stakeholders are CNOOC 51% interest, operator Kerr-McGee China Petroleum Ltd. 40% interest, and Sino-American Energy Corp, a subsidiary of Ultra Petroleum Corp., 9% interest.
EOR program proceeds in LAK Ranch field
Ivanhoe Energy Inc. and Derek Oil & Gas Corp., both of Vancouver, BC, commenced continuous steaming operations at the enhanced oil recovery pilot program in LAK Ranch oil field in Weston County, Wyo.
Production from the pilot well increased to 60 b/d of oil from 10 b/d in the first 6 days of continuous operations. The oil is being sold for $57/bbl. Three vertical steam injection wells were drilled in late August and September above existing horizontal wells. The effects of steam on the pay section will be measured to evaluate the effectiveness of the process, with volumes and quality of steam monitored and adjusted as necessary.
Production improvements are expected over the next several months. Derek Oil & Gas holds a 53% interest in the Powder River basin field. Ivanhoe Energy currently holds 42%, and an unnamed party holds the remaining 5%. ✦
Processing - Quick Takes
Gasco lets contract for Habshan plant expansion
Abu Dhabi Gas Industries Ltd. (Gasco) let an engineering, procurement, construction, and commissioning services contract to Fluor Corp. for the planned 1.3 bcfd expansion of the 1.04 bcfd Habshan gas complex in Abu Dhabi.
The nearly $1 billion contract includes the installation of two sulfur-recovery units with a total capacity of 1,600 tons/day, installation of an acid gas enrichment unit, increasing the capacity of the pressure-boosting units to feed the additional associated gas from Bab oil field for processing, and upgrading the distributed control system (OGJ Online, May 18, 2004).
Fluor’s Camberley, UK, office is executing the work with assistance from Consolidated Contractors International Co., Athens, which will handle construction and other execution support services. The project is scheduled to be completed in 32 months.
Minnesota’s largest ethanol plant planned
US BioEnergy Corp. of Brookings, SD, plans to build Minnesota’s largest ethanol plant near Janesville in Waseca County.
When completed, the plant will produce 100 million gal/year of ethanol and 320,000 tons/year of distiller’s grains. It will process 37 million bushels/year of corn, most of which will come from within 40 miles of the plant. US BioEnergy has two plants under construction: US Bio Albert City, a 100 million gal/year plant in Iowa; and US Bio Superior Corn, a 45 million gal/year plant near Woodberry, Mich. It is seeking additional sites.
According to the Renewable Fuels Association, there are currently 91 ethanol plants in the US with the capacity to produce more than 4 billion gal/year of ethanol. There are 20 ethanol plants and three major expansions under construction with a combined capacity exceeding 1.1 billion gal/year.
CPC’s Hainan refinery to start up by mid-2006
China Petrochemical Corp. reported it will start operations at a new refinery in southern China by mid-2006, according to a senior official.
Wang Jiming, CPC deputy chairman, said the plant in Hainan Province will start operations in June 2006. The plant’s production of 7 million tonnes/year of oil and chemical products will help to meet demand growth in Hainan and the Pearl River Delta region.
Construction of the refinery was launched in April 2004. Total investment for the plant is estimated at $1.23 billion.
Dow to build naphtha plant in Thailand
Dow Chemical Co. has teamed with Siam Cement PLC, Thailand’s largest industrial group, to build a $1.1 billion naphtha-cracking plant in Rayong province on Thailand’s eastern coast.
Under the signed letter of intent, Siam Cement holds a 67% stake in the scheme, which will be capable of producing 900,000 tonnes/year of ethylene and 800,000 tpy of propylene, using naphtha, condensate, and LPG as raw materials.
Construction of the plant, to be built 220 km southeast of Bangkok, is expected to commence early next year and is scheduled for operation start-up in 2010, Siam Cement said.
In an associated project, Siam Cement alone will invest $400 million in a new downstream facility using olefins derived from the cracker. This plant will be capable of producing 300,000 tpy of high-density polyethylene and 400,000 tpy of polypropylene, also starting in 2010.
Siam Cement already operates an existing naphtha-cracking plant in Rayong capable of producing 800,000 tpy of ethylene and 400,000 tpy of propylene. ✦
Transportation - Quick Takes
Kazakhstan-China oil pipeline completed
China National Petroleum Corp. and Kazakhstan’s National Petroleum & Natural Gas Co. have completed construction of the 1,000-km Atasu-Alashankou oil pipeline.
The new line, which extends from Atasu in Kazakhstan’s central Karaganda region through the Alashankou rail crossing with China’s western province of Xinjiang, is designed to carry 140 million bbl/year of crude from Kazakhstan to China starting Jan. 1, 2006.
In October, Kazakh Prime Minister Danial Akhmetov said the Atasu-Alashankou pipeline also could be used by Russian oil companies.
Russian state-owned oil company Rosneft, which currently transports oil to China by rail, has applied for permission to transport 1.2 million tonnes of oil via the Kazakhstan-China pipeline in 2006. OAO Lukoil also is said to have shown interest in the pipeline.
Meanwhile, Chinese state media said the Altaw Pass, where the final link in the pipeline was completed, is expected to become a hub for railway, road, and pipeline networks for the remote region in China’s northwest.
Work on the Ras Laffan Liquefied Natural Gas Co. Ltd. III (RasGas III) LNG megaproject was officially launched in Doha, reported Qatari joint venture partners Qatar Petroleum, 70%, and ExxonMobil Ras Laffan (III) Ltd., 30%.
RasGas III is an expansion of LNG production facilities operated by RasGas Co. Ltd. at Ras Laffan Industrial City in the northeastern part of Qatar (OGJ, Oct. 3, 2005, Newsletter). The project, expected to cost $13-14 billion, will bring to seven the total number of trains operated by RasGas.
RasGas III involves the design, construction, and operation of two LNG trains, Train 6 and Train 7, and all other facilities associated with the development, production, transport, processing, treatment, liquefaction, storage, delivery, and sales of about 15.6 million tonnes/year of LNG and products such as LPG, condensates, gas, helium, and sulfur.
Qatar aims to produce 77 million tonnes/year of LNG by 2010.
The new project will be developed in two consecutive phases. Train 6 is expected to start production in second-half 2008; Train 7 should come on stream about a year later.
Each train will receive gas from 14 wells drilled from existing wellhead platforms in offshore North field.
RasGas III has ordered 12 LNG tankers for the RasGas III project from Hyundai Heavy Industries, Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering, and Samsung Heavy Industries. Daewoo is to build five tankers, Samsung, four, and Hyundai, three. Contracts for a further six LNG tankers for Train 7 are expected to be awarded by yearend.
Chevron to build natural gas storage facility
Chevron Global Gas said it filed an application Nov. 2 with the US Federal Energy Regulatory Commission to build an underground natural gas storage facility in northeastern Colorado near Brush in Morgan County.
The Windy Hill project will include four salt storage caverns with a total capacity of 6 bcf of gas.
Construction of the first two storage caverns is slated to begin as early as 2006. Chevron expects to provide service from the first two storage caverns in 2008, and the third and fourth storage caverns in 2010.
ConocoPhillips to ship on Keystone pipeline
TransCanada Corp.’s proposed 1,840-mile Keystone pipeline project received a boost Nov. 3 when ConocoPhillips signed a memorandum of understanding committing to ship crude oil on the pipeline.
The system is designed to transport 435,000 b/d of crude oil from Hardisty, Alta., to Patoka, Ill. (OGJ Online, Aug. 9, 2005). ConocoPhillips said the pipeline would further integrate its upstream assets in Canada with its Wood River, Ill., refinery.
At the same time, ConocoPhillips Pipe Line Co. signed the MOU, giving it the right to acquire as much as half ownership in the $2.1 billion pipeline.
The Keystone system will include about 1,100 miles of new pipeline in the US, 220 miles of new pipeline in Canada, and the conversion of 540 miles of existing TransCanada natural gas pipeline facilities to crude oil transmission (see map, OGJ, Feb. 21, 2005, Newsletter). Depending on additional shipper interest and support, there could be potential for other extensions at each end of the pipeline. ✦