OGJ Newsletter
Market Movement
EIA predicts higher prices for US oil, gas
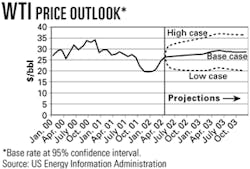
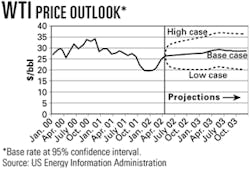
Pushed by a combination of psychological factors and market fundamentals, the price of US benchmark West Texas Intermediate (WTI) could reach almost $30/bbl in 2003, unless members of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries increase production in the last half of this year, said officials at the US Department of Energy's Energy Information Administration.
EIA officials assumed a boost in OPEC production is forthcoming to keep WTI prices below $30/bbl (see chart). But several OPEC ministers have since indicated they have no intention of changing current production quotas at their scheduled June meeting.
World oil prices continued to rise in April, marking the second consecutive month that the average price for OPEC's basket of seven benchmark crudes finished above $22/bbl. Prices for both the OPEC basket and North Sea Brent crude increased by $2/bbl on average from March levels. The price for WTI averaged more than $26/bbl in April, and closed above $27/bbl by month's-end, EIA officials said.
US oil supply
Average US oil production is expected to increase by 50,000 b/d, or 0.9%, this year to 5.89 million b/d. For 2003, a 0.6% increase is expected for an annual production rate average of 5.93 million b/d.
IEA predicted Alaska's oil production will increase by 3% this year and by another 5.4% in 2003 to account for 17.6% of total US oil output by that time. The 2003 increase will result from facilities expansion in the new North Slope field on the Colville River, Alpine. Another northern Alaska field, North Star, came on stream in the Beaufort Sea in November 2001 at a rate of more than 50,000 b/d. Production from Kuparuk River field-plus new production from the North Slope satellites West Sak, Tabasco, Tarn, and Meltwater-is expected by EIA officials to stay at an average of 220,000 b/d during 2002-03.
Lower 48 oil production is expected to increase by 21,000 b/d to 4.91 million b/d this year, followed by a decrease of 20,000 b/d in 2003. Oil production from Shell Oil Co.'s Brutus platform is expected to peak at 100,000 b/d this year. EIA officials said Mars, Troika, Ursa, Diana-Hoover, and Brutus fields in the Gulf of Mexico are expected to account for 9.2% of Lower 48 oil production by fourth quarter 2003.
Gasoline outlook
Meanwhile, EIA reported US regular grade gasoline prices stabilized at an average $1.40/gal at the pump in April, after surging by a record-breaking 23¢/gal during March. "It is likely that pump prices will soon rise after this current pause, since crude oil prices and demand for gasoline are both expected to increase over the next several months," officials said.
US gasoline prices averaged $1.70/gal in May 2001, a record high in current-dollar terms. However, EIA estimates US gasoline inventories were lower then by 10 million bbl, or 5%, than now.
"Assuming no major supply disruptions and assuming our base case of rising crude oil prices, gasoline pump prices could gain an additional 8-10¢/gal by June from the April average price of $1.40/gal," said EIA officials. "The summer average [April-September] is now expected to center around $1.44/gal, about 10¢/gal below the 2001 summer average."
Natural gas market
The US gas market this summer is projected to grow 4.4% above last summer's level because of lower gas prices and the slowly reviving economy.
US spot prices for natural gas have hovered above $3/Mcf since March, partly as a result of unusual weather patterns in March and April, EIA reported. March and much of April were colder than normal, but an unusual and intense heat wave also occurred in late April, producing a surge in electricity demand for cooling with subsequent increased demand for natural gas by the power sector. That was exacerbated by the rising price of crude due to market concerns over political tensions in the Middle East and a sense that the US economy is recovering more rapidly than previously expected, officials said. Incremental new capacity of gas-burning power plants, both proposed or under construction, also is adding to gas demand growth.
Meanwhile, natural gas production, as well as drilling and exploration, have recently fallen off, resulting in a less rosy supply outlook for the near term.
Industry Scoreboard
null
null
null
Industry Trends
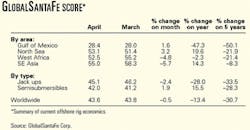
WORLDWIDE DRILLING MARKETS are firming up. Profitability of mobile rigs drilling in the Gulf of Mexico improved in April, ending a 10-month decline, said officials of GlobalSantaFe Corp., Houston, one of the most active offshore drilling contractors.
"The Gulf of Mexico SCORE [Summary of Current Offshore Rig Economics] hit its inflection point in April, reversing a 10-month downturn as day rates responded to improving utilization for certain jack up rig classes," said C. Stedman Garber Jr., president and CEO of GlobalSantaFe.
The SCORE rating for US gulf rigs increased by 1.6% to 28.4 in April, down 47.3% from year-ago levels and 50.1% from the past 5 years. Although the biggest single market for offshore drilling rigs, the gulf has the lowest SCORE rating at present (see table).
"While the offshore rig markets in Southeast Asia and West Africa remain moderately strong, there has been some mild erosion in jack up day rates," said Garber. "We expect the day rate declines in West Africa to abate as the gulf rig market continues to tighten, decreasing the incentive for gulf-based rigs to compete for work there." The company's monthly SCORE report compares the profitability of current day rates for mobile offshore drilling rigs to those at the 1980-81 peak of the offshore drilling cycle when new contract day rates equaled daily cash operating costs plus $700/day for each $1 million invested in a rig.
BUT THE BENZENE market reports another picture. The year 2001 will go down as one of the worst years for benzene demand, said a Chemical Market Associates Inc. study. However, conditions are in place to reverse that trend and firm up demand within 4 years.
Inventory destocking and the worldwide economic slowdown resulted in a 3% global contraction in benzene demand in 2001-the first such contraction on a global basis since 1982, CMAI said. North America was hit the hardest, with a 15% demand reduction in the US. Before 2001, world benzene demand growth was about 5%/year, CMAI said, but the 2001 demand decline pulled the average down to 3.5%/year during 1996-2001.
Government Developments
THE US ENVIRONMENTAL Protection Agency has called for public comment on a proposed rule governing air emissions from Category 3 marine diesel engines that power much of the world's merchant fleet.
The 139-page document addresses a number of complex technical issues. While seeking comment on emissions standards for US flag vessels, it also conforms those standards to the limits on nitrogen oxide emissions in Annex VI of the International Convention on the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL)-with some notable exceptions.
"By announcing the intention of the [US] government to seek Senate ratification of Annex VI, EPA has taken a major step [toward] preserving a US role in promoting global air quality improvements," said Peter Swift, managing director of the International Association of Independent Tanker Owners (Intertanko), Oslo, which has been pushing hard for uniform international standards as provided in MARPOL's Annex VI.
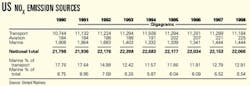
Although United Nations data show that marine source air pollution represents only a small percent of overall air emissions (see table)-EPA notes that Category 3 marine diesels contribute only 1-2% of the total US NOx output-Intertanko's council stresses the need for international limits on ship emissions. Many of the world's major maritime nations agreed to that treaty in 1997, but at least 15 nations that control over 50% of the world's shipping tonnage have not ratified it. The international shipping industry and its engine suppliers already comply, on a voluntary basis, with the Annex VI NOx requirements for new vessels. Intertanko's council has recommended that association members also adopt the association's VOCON operational procedure to reduce vapor emissions from tankers' cargo tanks during transportation.
PERU'S GOVERNMENT has authorized its energy ministry to appoint an ombudsman for the $1.3 billion Camisea natural gas project 500 km east of Lima on the eastern slopes of the Andes.
Energy Minister Jaime Quijandria said the initiative for the appointment came from the Inter-American Development Bank (IADB), following a successful experience with an ombudsman on the pipeline built to transport gas from Bolivian fields to Brazil.
IADB-together with the Andean Development Corp. and international banks-plans to finance $500 million of the Camisea project.
Quick Takes
MARATHON OIL CO., Houston, announced an open season ending Oct.15 for its proposed 675 km Symphony natural gas pipeline in the North Sea.
The proposed open-access contract carrier, which would extend from the Brae-Miller complex in the UK North Sea to the Bacton terminal in Suffolk, northeast of London, is expected to move some 900 MMcfd of gas (OGJ, Mar. 11, 2002, p. 8).
During the open season, Marathon will meet with prospective gas owners and field operators to outline pipeline plans and solicit input on the types of services sought. Gas owners, marketers, and operators also will be invited to offer gas volumes and contract for capacity on the pipeline.
Marathon says the pipeline could begin operating in 2005.
The Marathon-operated Brae field complex and the UK Miller and Britannia complexes are among the largest gas processing and transportation facilities in the UK North Sea.
Brae and Heimdal facilities have significant compression and processing capacity, and their close proximity to the Norwegian-UK border would help in gathering new gas supplies and could in time act as price reference points, Marathon said.
Centrica PLC, a UK-based natural gas retail marketer and producer, has agreed to support the project as a potential gas purchaser.
Other pipeline progress is occurring in New York. Iroquois Pipeline Operating Co. (IPOC), Shelton, Conn., awarded a contract to Horizon Offshore Inc., Houston, to construct and test the offshore portion of Iroquois's Eastchester pipeline extension project. The section consists of 35 miles of 24-in. line extending from landfall at Northport, Long Island, through Long Island Sound and into the East River at a point in South Bronx in New York City. Horizon is developing construction procedures and preparing equipment for mobilization in September. The offshore project is scheduled for completion by April 2003.
The project is part of the $170 million Eastchester expansion, which will supply 230 MMcfd of gas from Western Canada to the Consolidated Edison Co. gas grid. (OGJ Online, Apr. 30, 2000). Iroquois expects to begin construction on the onshore New York state facilities this quarter, with the whole Eastchester expansion to be placed into service in winter-spring 2002-03.
Meanwhile, Horizon Offshore also will begin work late this quarter on a contract received last month from Petroleos Mexicanos for pipeline system rehabilitation in Cantarell field in the Bay of Campeche off Mexico. Horizon will repair riser expansion curves, pig and test the repaired segments and related existing facilities, install topside spools and valves, perform line stabilizations, repair pipeline crossings, recover out-of-service lines, and trench the repaired segments and existing pipeline installations.
The Atlantic Horizon derrick barge, Gulf Horizon lay barge, and Pearl Horizon diving support vessel will be utilized on the project. Construction is scheduled to begin in late second quarter.
THE US COAST GUARD May 10 said it wants to standardize vessel response plans for oil tankers. Officials said proposed rule changes, 5 years in the making, will clarify which salvage and marine firefighting services are required in vessel response plans.
US officials said the proposed changes would ensure that "appropriate salvage and marine firefighting resources are identified and [are] available for responding to incidents up to and including the worst-case scenario."
Under the proposal, vessel operators must identify salvage and firefighting companies that can meet existing oil spill regulations under the Oil Pollution Act of 1990. Companies contracted by the vessel operators must be able to perform specialized tasks detailed by the Coast Guard, including emergency towing, onsite fire and structural-stability assessments, and salvage operations.
The Coast Guard estimates the rule will prevent 87,282 bbl of oil from being spilled, resulting in a cost-effectiveness of $5,634 for each barrel not spilled: "This means it costs society $5,600 to keep each barrel of oil from being spilled into the water."
The cost to industry to implement the rules, based on a 30-year time period, will be $491 million. Firefighting and salvage companies will probably spend about $127.9 million ($111.7 million in 2002 dollars) in up-front costs to buy equipment when the rule is finalized in 2003. The Coast Guard anticipates the capital and annual costs incurred by salvage and firefighting companies will be largely passed on to vessel planholders through retainer fees or increased service costs.
The proposed rulemaking will also set new response time requirements for each of the required salvage and marine firefighting services.
The Coast Guard plans to hold several public meetings before Aug. 8, when comments are due. Meeting dates and locations will be published in the Federal Register at least 30 days before the meetings, officials said.
AN ENHANCED GEOTHERMAL SYSTEM (EGS) to boost production of geothermal energy in California will receive $4.5 million over the next 5 years from the US Department of Energy. The University of Utah's Energy & Geoscience Institute (UU-EGI) and Caithness Energy LLC of New York City jointly will develop the $12 million system.
The EGS is expected to more than double the amount of geothermal energy economically recoverable in the US and extend the productive life of existing geothermal fields, DOE said.
UU-EGI and Caithness will pump water under high pressure into a portion of Coso geothermal field to fracture subsurface rocks and create channels for hot water to move from the geothermal reservoir to existing geothermal wells.
Sec. of Energy Spencer Abraham said that improving productivity of the field, 25 miles north of Ridgecrest, Calif., on the China Lake Naval Air Weapons Station, would add about 15 Mw of electrical capacity-"enough to power 11,250 homes"-to the 270 Mw now generated at Coso.
The Coso geothermal plant operates under agreements with the US Navy and the US Department of Interior's Bureau of Land Management, paying production royalties to the federal government.
Other awards will follow. The EGS cooperative agreement is the first award in a three-part program. DOE is seeking applications for Stage Two, which is designed to improve economically unproductive geothermal fields. During Stage Three, DOE will develop technology for finding new geothermal fields where EGS technology can be applied.
STATOIL ASA has found condensate and light oil in two wells drilled in the Tampen area near Gullfaks and Statfjord fields in the Norwegian North Sea. Both wells lie on production License 152. Exploration well 33/12-8S was drilled on the Dole prospect, while well 33/12-8A was drilled on the Ole prospect.
The wells confirmed hydrocarbons in Middle Jurassic rock. Because of similarities between the discoveries and Rimfaks and Gullveig producing fields, the wells were not production-tested. Well 33/12-8S was drilled to 3,350 m below mean sea level, and 33/12-8A was drilled to 3,369 m. The latter was temporarily abandoned and will come on stream at a later stage.
The Borgland Dolphin semisubmersible drilled both wells.
"We have started a project to evaluate potential tie-back points for the new finds," said Bengt Beskow, Statoil's exploration manager for the Tampen complex. "If they are profitable, we expect them to produce from 2004," he said. The finds are about 16 km from both the Statfjord B and Gullfaks A platforms. The distance between Ole and Dole is about 1,700 m.
Statoil is evaluating two development alternatives: The finds could be tied back via subsea templates on Gullfaks South satellite field and then on to Gullfaks C, or they could be tied back to the Statfjord B platform.
Statoil will be sole operator for the Tampen complex when the group takes over Snorre, Visund, Vigdis, and Tordis fields from Norsk Hydro AS on Jan.1, 2003. The group therefore wants to search for and develop small finds in the area to extend production from Tampen platforms.
The licensees in License 152 are Statoil 58.89%, Petoro (formerly state holdings group SDFI) 30%, and ExxonMobil Corp. 11.11%. Statoil has entered into an agreement to assume ExxonMobil's stake retroactive from Jan.1. Authorities are expected to approve the agreement before midyear.
Elsewhere on the exploration front, Amerada Hess Corp. has discovered oil on its Devils Island prospect on Garden Banks Block 344 in the Gulf of Mexico. The GB 344 No. 4 well encountered more than 100 ft of net oil pay in a single, high-quality reservoir. The well was drilled to 24,525 ft TD in 2,300 ft of water. The discovery is 135 miles off Louisiana, 12 miles southwest of Baldpate field. Amerada Hess is operator of the Devils Island prospect with 80% interest. EEX Corp., Houston, owns 20% interest.
In deeper water activity, Unocal Rapak Ltd., subsidiary of Unocal Corp., El Segundo, Calif., has drilled its fifth successful well in deepwater Ranggas oil field in the southern part of the Rapak production-sharing contract off East Kalimantan, Indonesia. The Ranggas-5 appraisal well was drilled in 5,412 ft of water to 11,858 ft TVD, encountering 203 ft of net oil pay and 618 ft of net gas pay. The well is 1.5 miles north of the Ranggas-1 discovery well and 0.7 mile south of the Ranggas-4 well, which was recently tested at 8,158 b/d of oil and 6.4 MMcfd of natural gas from a single interval. "The [Ranggas-5] well penetrated more net pay than any other well in Unocal Indonesia's long history," said Brian Marcotte, president of Unocal Indonesia Co. "Because of our successful appraisal drilling program, we have initiated engineering and development studies for the field." Unocal Rapak is operator of the Rapak PSC, holding an 80% working interest, while Lasmo Rapak Ltd., a subsidiary of ENI SPA, holds 20%.
The US Bureau of Land Management will conduct an oral oil and gas lease auction June 4 in Cheyenne, Wyo. BLM will offer 95 parcels totaling 87,120 acres of federal lands in Wyoming and Nebraska. Auction rules call for a $2/acre minimum bid in bonuses on any parcel, BLM said. This means a buyer will pay the bid price for the right to obtain the federal lease in addition to a standard $1.50/acre rental on the lease. BLM will also charge winning bidders $75/parcel to help cover administrative costs. Leases have a 10-year term but can be continued as long as oil or gas is produced in paying quantities for royalty collection purposes. BLM last month published and mailed a notice of sale to potential federal oil and gas lease bidders. It contains a complete list of the parcels, conditions of the sale, and lease stipulations, also available at BLM's web site.
SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO. has awarded Paris-based Technip-Coflexip a lump sum, turnkey contract for the design and construction of a sulfur recovery plant at its refinery in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Under terms of the contract, Technip-Coflexip will provide two new, 70 tonne/day sulfur recovery units, sulfur tankage, truck-loading facilities, a new sour-water stripper unit, and a new amine-treating unit. The work also includes upgrading and modification of existing facilities.
Turnkey services will include project management, detail engineering, procurement of equipment and materials, construction management, construction, precommissioning, and assistance to commissioning.
The sulfur recovery units will improve the local environment by reducing sulfur-dioxide emissions. The recovered liquid sulfur will be pumped to storage tanks and loaded into trucks for export.
Technip-Coflexip 's engineering center in Abu Dhabi will carry out the overall project, and the group's local affiliate Technip Saudi Arabia will perform the construction.
KERR-McGEE CORP., Oklahoma City, has approved a development plan for its discoveries on Block 04/36 in Bohai Bay, China.
Pending regulatory and partner approvals, development will include exploitation of CFD 11-1, CFD 11-2, and CFD 2-1 fields, using a leased, centrally located, floating production, storage, and offloading (FPSO) vessel along with fixed platforms that will serve as drillsites for dry wellheads.
The FPSO, which will be fabricated in China, will be located in 75 ft of water, 50 miles offshore. It will have the capacity to process more than 60,000 b/d of oil and will have a storage capacity of 1 million bbl. Kerr-McGee estimates area reserves at more than 150 million bbl. With government and partner approval of the development program, initial production could begin by yearend 2004, with peak production projected to exceed 50,000 b/d by mid-2005.
Kerr-McGee operates Block 04/36 with an 81.82% foreign contractor's interest. Its partners are China National Offshore Oil Corp., Beijing, and Sino-American Energy Corp., a wholly owned subsidiary of Houston-based Ultra Petroleum Corp.
Kerr-McGee has five Bohai Bay discoveries and a number of identified prospects within its three operated licenses.
Its exploration program includes discoveries CFD 12-1 and CFD 12-1S on the adjacent 05/36 block, which Kerr McGee operates with a 50% foreign contractor's interest. The company continues to evaluate Block 05/36 and plans additional appraisal drilling this year along with several more exploratory prospects in Bohai Bay.